Warfarin-Induced Skin Necrosis Despite Enoxaparin Bridging Therapy
- PMID: 35145788
- PMCID: PMC8808085
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.20883
Warfarin-Induced Skin Necrosis Despite Enoxaparin Bridging Therapy
Abstract
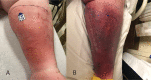
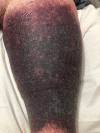
Skin necrosis is a rare albeit severe complication of warfarin use for anticoagulation, resulting in significant morbidity and mortality. Here, we present the case of a 58-year-old woman who developed erythema and pain in her left leg two weeks after initiation of warfarin therapy with concomitant early administration of heparin for a deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Subsequently, the erythema progressed to skin necrosis, and a diagnosis of warfarin-induced skin necrosis (WISN) was suspected. Warfarin was discontinued, and unfractionated heparin was commenced. The simultaneous presence of eosinophilia pointed toward an associated drug-related hypersensitivity reaction. Dexamethasone was added to the medication regimen. The patient was discharged on a factor Xa inhibitor and prednisone. Recognizing WISN is crucial in patients receiving anticoagulation. The diagnosis can be particularly challenging in cases when bridging anticoagulation has been previously completed. Early diagnosis and drug discontinuation are critical to ensuring a favorable prognosis. Steroids may also play a role in the treatment of this condition if an associated drug hypersensitivity is identified.
Keywords: bridging anticoagulation; drug rash; drug-induced hypersensitivity; enoxaparin; warfarin therapy; warfarin-induced skin necrosis.
Copyright © 2022, Wali et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Warfarin skin necrosis: local and systemic factors. Ad-El DD, Meirovitz A, Weinberg A, Kogan L, Arieli D, Neuman A, Linton D. Br J Plast Surg. 2000;53:624–626. - PubMed
-
- Warfarin-induced skin necrosis. Nazarian RM, Van Cott EM, Zembowicz A, Duncan LM. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:325–332. - PubMed
-
- Coumarin necrosis--a review of the literature. Cole MS, Minifee PK, Wolma FJ. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3278401/ Surgery. 1988;103:271–277. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
