Exercise-Induced Bronchospasm in Elite Athletes
- PMID: 35145802
- PMCID: PMC8807463
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.20898
Exercise-Induced Bronchospasm in Elite Athletes
Abstract
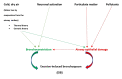
Exercise is one of the most common triggers of exercise-induced bronchospasm (EIB), with less trained athletes showing more symptoms. Exercise-induced bronchospasm is a common and frequent problem among elite athletes with obvious implications on competing performance, health, and quality of life. Classical pathways in the development of EIB in this population include the osmotic and the thermal theory as well as the presence of epithelial injury and inflammation in the airway. Moreover, neuronic stimulation has been suggested as a potential modulator of EIB in elite athletes. In this category of population, the diagnosis of EIB is a serious challenge, especially as spirometry before and after bronchodilation is not diagnostic and specific tests are required. To date, there is no organized screening in asymptomatic elite athletes to detect EIB. This review aims to summarize the pathophysiology, clinical manipulations, and therapeutic approach of EIB in elite athletes. We searched for published studies related to the aim of this study. Exercise-induced bronchospasm is a serious and common disorder in elite athletes, and its symptoms are nonspecific with a need to confirm the diagnosis with specific tests.
Keywords: airway dehydration; airway hydration; athletic asthma; cardiopulmonary exercise test; elite athletes; exercise induced bronchoconstriction; exercise induced bronchospasm.
Copyright © 2022, Pigakis et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology Work Group report: exercise-induced asthma. Weiler JM, Bonini S, Coifman R, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:1349–1358. - PubMed
-
- Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction: a clinical approach. Papaioannou A, Bartziokas K, Loukides S, et al. http://www.pneumon.org/Exercise-Induced-Bronchoconstriction-A-clinical-a... Pneumon. 2014;27:139–146.
-
- An overview of asthma and airway hyper-responsiveness in Olympic athletes. Fitch KD. Br J Sports Med. 2012;46:413–416. - PubMed
-
- Proceedings of the first Jack Pepys Occupational Asthma Symposium. Chan-Yeung M, Malo JL, Tarlo SM, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;167:450–471. - PubMed
-
- Work group report: perspectives in diagnosis and management of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in athletes. Greiwe J, Cooke A, Nanda A, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2020;8:2542–2555. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
