Effect of Lavender (Lavandula angustifolia L.) syrup on olfactory dysfunction in COVID-19 infection: A pilot controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 35145890
- PMCID: PMC8801216
- DOI: 10.22038/AJP.2021.18420
Effect of Lavender (Lavandula angustifolia L.) syrup on olfactory dysfunction in COVID-19 infection: A pilot controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Objective: The effect of lavender syrup on COVID-19-induced olfactory dysfunction (OD) has been assessed in this study.
Materials and methods: This pilot clinical trial was conducted in Gonbad-E-Kavoos (Golestan province, Iran). Twenty-three outpatients with COVID-19 and OD in lavender group took 9 ml of lavender syrup/bid for 3 weeks along with the standard COVID-19 treatments and 20 patients in control group took only standard COVID-19 treatments. The severity of OD was assessed by the visual analogue scale (VAS). Data analysis was performed by Friedman and Mann-Whitney tests using SPSS software.
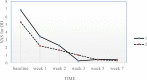
Results: The mean± standard deviation of age was 36.6±9.1, and 42.6±10.4 years (p=0.05), and the duration of symptoms was 7.4±3.5, and 7.5±3.4 days (p=0.98) in the lavender and control group, respectively. The VAS score for OD decreased from 6.8±3.04 to 0.26±0.86 in the lavender group and from 5.3±3.4 to 1±2.61 in the control group. Although, VAS for OD was significantly decreased in both groups (p<0.001), the amount of VAS decrease was 6.6±2.9 scores in the lavender group, and 4.3±4 in the control group (p=0.03). No side effects were observed in the lavender group.
Conclusion: The present study showed that lavender syrup is an effective treatment for COVID-19-induced OD. It is suggested to conduct further studies with larger sample size.
Keywords: Anosmia; COVID-19; Herbal medicine; Lavendula; Persian medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lavender (Lavandula angustifolia) syrup as an adjunct to standard care in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: An open-label, randomized, controlled clinical trial.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2023 Jul-Aug;13(4):400-411. doi: 10.22038/AJP.2022.21606. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2023. PMID: 37663382 Free PMC article.
-
Lavender and dodder combined herbal syrup versus citalopram in major depressive disorder with anxious distress: A double-blind randomized trial.J Integr Med. 2020 Sep;18(5):409-415. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2020.06.002. Epub 2020 Jun 15. J Integr Med. 2020. PMID: 32739466 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of inhaled Lavandula angustifolia Mill. Essential oil on sleep quality, quality of life and metabolic control in patients with diabetes mellitus type II and insomnia.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Apr 6;251:112560. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112560. Epub 2020 Jan 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31931160 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and tolerability of Lavandula angustifolia in treating patients with the diagnosis of depression: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.J Complement Integr Med. 2021 Aug 23;20(1):81-91. doi: 10.1515/jcim-2020-0498. eCollection 2023 Mar 1. J Complement Integr Med. 2021. PMID: 34420270 Review.
-
Effects of lavender on anxiety: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Phytomedicine. 2019 Dec;65:153099. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153099. Epub 2019 Sep 26. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31655395
Cited by
-
Traditional Chinese medicine for post-viral olfactory dysfunction: A systematic review.Integr Med Res. 2024 Jun;13(2):101045. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2024.101045. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Integr Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38831890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenolic compounds versus SARS-CoV-2: An update on the main findings against COVID-19.Heliyon. 2022 Sep 20;8(9):e10702. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10702. eCollection 2022 Sep. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36157310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The use of Ephedra herbs in the treatment of COVID-19.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2023 May-Jun;13(3):231-239. doi: 10.22038/AJP.2022.21607. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2023. PMID: 37654998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of COVID-19 manipulation by selective ACE inhibitory compounds of Potentilla reptant root: In silico study and ADMET profile.Arab J Chem. 2022 Jul;15(7):103942. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.103942. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Arab J Chem. 2022. PMID: 35502159 Free PMC article.
-
The adjuvant therapy of edible herbal product including colchicum bulb, olive leaf, black cumin seeds, lavender flower, and ginger rhizome on the outcome of patients with severe and critical COVID-19: A double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2024 Nov-Dec;14(6):686-698. doi: 10.22038/AJP.2024.24633. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2024. PMID: 40259958 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acikalin A, Gulen M, Kara B, Icme F, Cagliyan CE, Satar S. Anticholinergic syndrome and supraventricular tachycardia caused by lavender tea toxicity. Keio J Med. 2012;61:66. - PubMed
-
- Aghili Khorasani MH. Makhzan-al-Advieh . Tehran, Sabz Arang; 2012. p. 140.
-
- Amin Gh, Bozorgi M, Salari H, Khalaj A, Zolphaghari B, Rahimi R. Ostokhodus. Trad Med Islam & Iran. 2019;10:89–96.
-
- Basch E, Foppa I, Liebowitz R, Nelson J, Smith M, Sollars D. Lavender (Lavandula angustifolia Miller) J herb pharmacother. 2004;4:63–78. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources