CD70 in Thymic Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Potential Diagnostic Markers and Immunotherapeutic Targets
- PMID: 35145909
- PMCID: PMC8821901
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.808396
CD70 in Thymic Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Potential Diagnostic Markers and Immunotherapeutic Targets
Abstract
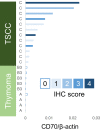
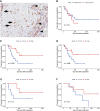
CD70 - a ligand protein of CD27 on lymphocytes - is expressed in a large spectrum of malignancies. It is an attractive target for antibody-based therapy and several clinical trials are currently being conducted. However, there is no evidence regarding the expression of CD70 and its relationship with expression of programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) and CD27+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues of thymic tumors. FFPE tissues of thymic squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC) (operative specimens, n = 31; biopsy specimens, n = 11), thymoma (n = 60), thymic carcinoid (n = 3), and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) (n = 30) were analyzed immunohistochemically. Immunoreactivity for CD70 was semi-quantitatively scored according to the proportion of positive tumor cells. Moreover, the densities of CD27-positive intratumoral TIL (iTIL) and stromal TIL of TSCC were assessed and survival was compared. Most TSCC cases (87%; 27/31) were CD70-positive. In contrast, all thymoma and thymic carcinoid cases were CD70-negative. In LSCC cases, CD70-positivity was significantly lower than TSCC cases (20%; 6/30). Biopsy and resected specimens obtained from the same patients demonstrated a consistent staining pattern (6/6 patients). The proportion of CD70-positive TSCC was comparable with those of CD5 (87%) and CD117 (90%). Correlation between CD70 and PD-L1 expression score was observed. There was no significant difference in survival between the CD70-high and CD70-low expression groups. Meanwhile, patients with CD27-positive iTIL-high tumors exhibited better survival than those with iTIL-low tumors. This tendency was weaker in the CD70-high subset. CD70 immunohistochemistry is useful in diagnosing TSCC. CD70 may prevent anti-tumor immunity via CD27. Immunotherapy targeting the CD70-CD27 axis may be a promising option for the treatment of TSCC.
Keywords: CD27; CD70; immunohistochemistry; thymic carcinoma; tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte.
Copyright © 2022 Kashima, Hishima, Okuma, Horio, Ogawa, Hayashi, Horiguchi, Motoi, Ushiku and Fukayama.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

