Effect of Dexmedetomidine-Assisted Intravenous Inhalation Combined Anesthesia on Cerebral Oxygen Metabolism and Serum Th1/Th2 Level in Elderly Colorectal Cancer Patients
- PMID: 35145993
- PMCID: PMC8821817
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2021.832646
Effect of Dexmedetomidine-Assisted Intravenous Inhalation Combined Anesthesia on Cerebral Oxygen Metabolism and Serum Th1/Th2 Level in Elderly Colorectal Cancer Patients
Abstract
Objective: To observe the effect of dexmedetomidine-assisted intravenous inhalation combined anesthesia on cerebral oxygen metabolism and serum Th1/Th2 levels in elderly patients with colorectal cancer.
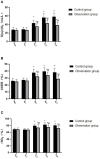
Method: From April 2018 to May 2020,100 elderly patients undergoing elective laparoscopic radical resection of colorectal cancer were prospectively selected and randomly divided into observation group and control group. Before induction of anesthesia, the loading dose of dexmedetomidine was given at 0.5 μg/kg, and the infusion time was 15 min. After tracheal intubation, 0.4 μg/kg/h dexmedetomidine was continuously pumped, and the infusion was stopped 40 min before the end of the operation. In the control group, the same amount of 0.9% sodium chloride was injected intravenously in the same way. 30 min before induction of anesthesia (T0), immediately before induction of anesthesia (T1), immediately after tracheal intubation (T2), 40 min before operation (T3), and immediately after operation (T4), record the blood oxygen content of the artery and internal jugular vein Difference (D(a-jv)O2), brain oxygen uptake rate (COER%), brain oxygen saturation (rSO2) mean. VAS scale, Ramsay scale, MoCA scale were taken at 6, 12, 24, and 48 h postoperatively to evaluate analgesia, sedation, and cognitive function. And monitor the levels of interferon-γ (IFN-γ), interleukin-4 (IL-4), myelin basic protein (MBP), neuron-specific enolase (NSE) and S100β. The occurrence of restlessness and adverse reactions during the recovery period of the two groups were compared.
Result: The levels of D(a-jv)O2, COER%, and rSO2 in the control group and observation group were higher than the preoperative basic values at T2, T3, and T4 (P < 0.05); The levels of D(a-jv)O2, COER%, and rSO2 in the observation group were lower than those in the control group at T2, T3, and T4 (P < 0.05). The VAS score and Ramsay score of the observation group were lower than those of the control group at 6, 12, 24, and 48 h after surgery, while the MoCA score was higher than that of the control group (P < 0.05). In addition, the serum IFN-γ, MBP, NSE and S100β levels of the observation group were lower than those of the control group (P < 0.05), and the ratio of IFN-γ/IL-4 was higher than that of the control group (P < 0.05). The overall incidence of adverse reactions in the observation group was lower than that in the control group [32.0% (16/50) vs. 12.0% (6/50), P < 0.05].
Conclusion: Dexmedetomidine-assisted combined intravenous and inhalation anesthesia is beneficial to reduce perioperative cerebral oxygen metabolism and improve postoperative immunosuppression in elderly patients with colorectal cancer. It has a certain protective effect on nerve injury after operation, thus improving the cognitive function of patients and reducing the occurrence of adverse reactions.
Keywords: cerebral oxygen metabolism; cognitive impairment; dexmedetomidine; elderly patients with colorectal cancer; immune function.
Copyright © 2022 Tang, Liu, Huang, Ding, Tan and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

