Analytical performance of a new immunoturbidimetric D-dimer assay and comparison with available assays
- PMID: 35146238
- PMCID: PMC8818496
- DOI: 10.1002/rth2.12660
Analytical performance of a new immunoturbidimetric D-dimer assay and comparison with available assays
Abstract
Background: The routine D-dimer quantification to exclude venous thromboembolism has led to the development of many assays, the usefulness of which depends on their reliability and performance.
Objective: We evaluated the analytical performances of the immunoturbidimetric Yumizen G DDi 2 assay (HORIBA Medical, Montpellier, France) performed on the Yumizen G800 analyzer and compared it with other available D-dimer assays.
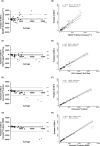
Methods: Within-run and between-run imprecision were evaluated using low- and high-level quality-control plasma samples. Interference due to hemolysis, icterus, lipemia, rheumatoid factor (RF), or heterophilic antibodies (human antimouse antibodies [HAMAs]) was evaluated by spiking plasma samples with hemolysate, bilirubin, Intralipid, RF, or HAMAs. The measurements obtained with the different D-dimer assays were compared using Passing-Bablok regression analysis and Bland-Altman plot method, using fresh citrated plasma samples collected from 66 consecutive routine patients with a wide range of D-dimer concentrations.
Results: Within- and between-run variation coefficients for the Yumizen G DDi 2 assay ranged from 1.7% to 5.8% and from 2.8% to 5.5%, respectively. Hemolysis and icterus did not have any effect up to 10 g/L hemoglobin and 300 mg/L bilirubin. Lipemia seemed to generate an underestimation of D-dimer concentration when the Intralipid concentration was >5 g/L. RF and HAMAs did not have any effect. The Passing-Bablok and Bland-Altman analyses showed small differences with other available D-dimer assays, which were more pronounced with increasing values.
Conclusions: Its analytical performances and main technical features indicate that the new Yumizen G DDi 2 assay is suitable for the rapid quantification of D-dimer in clinical hemostasis laboratories.
Keywords: bilirubin; hemolysis; hemostasis; immunoturbidimetry; thrombosis; venous thromboembolism.
© 2022 The Authors. Research and Practice in Thrombosis and Haemostasis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH).
Figures





Similar articles
-
Performance of the automated and rapid HemosIL D-Dimer HS on the ACL TOP analyzer.Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2008 Dec;19(8):817-21. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0b013e32830f1bae. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2008. PMID: 19002050
-
Evaluation of the Innovance D-DIMER analytical performance.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2009;47(8):945-51. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2009.219. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2009. PMID: 19548843
-
Abbott D-dimer assay: analytical performance and diagnostic accuracy in management of venous thromboembolism.Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2024 Feb;84(1):53-61. doi: 10.1080/00365513.2024.2318616. Epub 2024 Feb 16. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2024. PMID: 38362664
-
D-dimer testing in the diagnosis of acute venous thromboembolism.Thromb Haemost. 1999 Aug;82(2):688-94. Thromb Haemost. 1999. PMID: 10605769 Review.
-
D-dimer for the diagnosis of venous thromboembolism.Curr Opin Hematol. 2000 Sep;7(5):296-301. doi: 10.1097/00062752-200009000-00007. Curr Opin Hematol. 2000. PMID: 10961580 Review.
Cited by
-
D-dimer Testing in Pulmonary Embolism with a Focus on Potential Pitfalls: A Narrative Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Nov 12;12(11):2770. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12112770. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428830 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Raskob GE, Angchaisuksiri P, Blanco AN, et al. Thrombosis: a major contributor to global disease burden. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34:2363‐2371. - PubMed
-
- Bounameaux H, de Moerloose P, Perrier A, Reber G. Plasma measurement of D‐dimer as diagnostic aid in suspected venous thromboembolism: an overview. Thromb Haemost. 1994;71:1‐6. - PubMed
-
- van der Graaf F, van den Borne H, van der Kolk M, de Wild PJ, Janssen GW, van Uum SH. Exclusion of deep venous thrombosis with D‐dimer testing–comparison of 13 D‐dimer methods in 99 outpatients suspected of deep venous thrombosis using venography as reference standard. Thromb Haemost. 2000;83:191‐198. - PubMed
-
- Di Nisio M, Squizzato A, Rutjes AWS, Büller HR, Zwinderman AH, Bossuyt PMM. Diagnostic accuracy of D‐dimer test for exclusion of venous thromboembolism: a systematic review. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5:296‐304. - PubMed
-
- Bjøri E, Johnsen HS, Hansen J‐B, Braekkan SK. D‐dimer at venous thrombosis diagnosis is associated with risk of recurrence. J Thromb Haemost. 2017;15:917‐924. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

