Mortality and disability reported after immunoglobulins or plasmapheresis treatment of Guillain-Barré syndrome
- PMID: 35146369
- PMCID: PMC8805471
- DOI: 10.53854/liim-2904-13
Mortality and disability reported after immunoglobulins or plasmapheresis treatment of Guillain-Barré syndrome
Abstract
Objective: To compare the clinical results (28-day mortality and disability at discharge) in patients with Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) treated with immunoglobulin or plasmapheresis at the Regional Lambayeque in Peru Hospital.
Patients and methods: Retrospective Cohort Study. Brighton criteria was used for diagnosing GBS, and modified Rankin scale (MRS) was employed for evaluating functional outcome. We used logistic regression for data analyses.
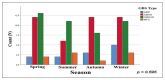
Results: A total of 142 cases of GBS diagnosed from 2011 to 2020 were included. GBS presented in a seasonal pattern; 60% of cases occurred in winter and spring. Motor variants (AMAN and AMSAN) accounted for 60% of cases, whereas only 8.5% of cases were typical GBS (AIDP). About 60% of patients were males, and 56% of cases corresponded to the age range of 20-59 years. Patients aged ≥60 years accounted for only 24% of total cases of GBS, but this group had a lethality of 58.3%. Although 28-day mortality was statistically similar in both treatment groups (plasmapheresis or immunoglobulin), we found a trend toward lower mortality in the plasmapheresis group (OR 0.78; 95% CI 0.62-0.97; p=0.062). We found no differences in terms of disability at discharge in GBS patients treated with plasmapheresis or immunoglobulin.
Conclusion: Mortality and functional outcome were statistically similar between patients treated with immunoglobulin or plasmatic exchange. However, there was a trend toward lower mortality in patients treated with plasmapheresis.
Keywords: Guillain-Barré syndrome; disability; mortality; therapy.
Copyright © 2016 - 2021 InfezMed.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest None to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Electrophysiological Pattern and Predictors of Functional Outcome of Patients with Guillain Barre Syndrome at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Pakistan.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2022 Mar;32(3):364-368. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2022.03.364. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2022. PMID: 35148591
-
Clinical features and real-world outcomes of Guillain-Barré syndrome in the Philippines.Neurol Res. 2021 Dec;43(12):995-1004. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2021.1948750. Epub 2021 Jul 6. Neurol Res. 2021. PMID: 34229572
-
Outcome of Guillain-Barré syndrome following intravenous immunoglobulin compared to natural course.Eur J Neurol. 2022 Oct;29(10):3071-3080. doi: 10.1111/ene.15500. Epub 2022 Aug 2. Eur J Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35837807
-
Guillain-Barré syndrome: epidemiology, pathophysiology and management.Drugs. 2004;64(6):597-610. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200464060-00003. Drugs. 2004. PMID: 15018590 Review.
-
[Guillain Barré syndrome in pediatrics].Medicina (B Aires). 2009;69(1 Pt 1):84-91. Medicina (B Aires). 2009. PMID: 19240005 Review. Spanish.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources