SLAMF7 engagement superactivates macrophages in acute and chronic inflammation
- PMID: 35148199
- PMCID: PMC8991457
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abf2846
SLAMF7 engagement superactivates macrophages in acute and chronic inflammation
Abstract
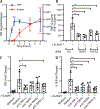
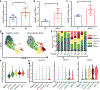
Macrophages regulate protective immune responses to infectious microbes, but aberrant macrophage activation frequently drives pathological inflammation. To identify regulators of vigorous macrophage activation, we analyzed RNA-seq data from synovial macrophages and identified SLAMF7 as a receptor associated with a superactivated macrophage state in rheumatoid arthritis. We implicated IFN-γ as a key regulator of SLAMF7 expression and engaging SLAMF7 drove a strong wave of inflammatory cytokine expression. Induction of TNF-α after SLAMF7 engagement amplified inflammation through an autocrine signaling loop. We observed SLAMF7-induced gene programs not only in macrophages from rheumatoid arthritis patients but also in gut macrophages from patients with active Crohn's disease and in lung macrophages from patients with severe COVID-19. This suggests a central role for SLAMF7 in macrophage superactivation with broad implications in human disease pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Nathan C, Ding A, Nonresolving Inflammation. Cell. 140 (2010), pp. 871–882. - PubMed
-
- Mulherin D, Fitzgerald O, Bresnihan B, Synovial tissue macrophage populations and articular damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and rheumatism. 39, 115–24 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Smiljanovic B, Grützkau A, Sörensen T, Grün JR, Vogl T, Bonin M, Schendel P, Stuhlmüller B, Claussnitzer A, Hermann S, Ohrndorf S, Aupperle K, Backhaus M, Radbruch A, Burmester GR, Häupl T, Synovial tissue transcriptomes of long-standing rheumatoid arthritis are dominated by activated macrophages that reflect microbial stimulation. Scientific reports. 10, 7907 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 AI148102/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067685/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UM2 AR067678/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007627/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR070253/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067681/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067688/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AR075850/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067689/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067690/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067677/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067694/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067679/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067676/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067691/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

