Immune imprinting, breadth of variant recognition, and germinal center response in human SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination
- PMID: 35148837
- PMCID: PMC8786601
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.01.018
Immune imprinting, breadth of variant recognition, and germinal center response in human SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination
Abstract
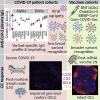
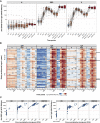
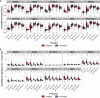
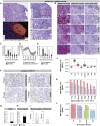
During the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, novel and traditional vaccine strategies have been deployed globally. We investigated whether antibodies stimulated by mRNA vaccination (BNT162b2), including third-dose boosting, differ from those generated by infection or adenoviral (ChAdOx1-S and Gam-COVID-Vac) or inactivated viral (BBIBP-CorV) vaccines. We analyzed human lymph nodes after infection or mRNA vaccination for correlates of serological differences. Antibody breadth against viral variants is lower after infection compared with all vaccines evaluated but improves over several months. Viral variant infection elicits variant-specific antibodies, but prior mRNA vaccination imprints serological responses toward Wuhan-Hu-1 rather than variant antigens. In contrast to disrupted germinal centers (GCs) in lymph nodes during infection, mRNA vaccination stimulates robust GCs containing vaccine mRNA and spike antigen up to 8 weeks postvaccination in some cases. SARS-CoV-2 antibody specificity, breadth, and maturation are affected by imprinting from exposure history and distinct histological and antigenic contexts in infection compared with vaccination.
Keywords: Astra Zeneca; BBIBP-CorV; BNT162b2; BioNTech-Pfizer; COVID-19; ChAdOx1-S; Delta variant; Gam-COVID-Vac; Moderna; SARS-CoV-2; SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern; Sinopharm; Sputnik V; antibodies; autopsy; endemic coronaviruses; imprinting; lymph node germinal center; mRNA-1273; vaccine.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests S.D.B. has consulted for Regeneron, Sanofi, Novartis, and Janssen on topics unrelated to this study and owns stock in AbCellera Biologics. K.C.N. reports grants from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), Food Allergy Research & Education (FARE), End Allergies Together (EAT), National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI), and National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS). K.C.N. is Director of FARE and World Allergy Organization (WAO) Center of Excellence at Stanford; Adviser at Cour Pharmaceuticals; Cofounder of Before Brands, Alladapt, Latitude, and IgGenix; National Scientific Committee member for the Immune Tolerance Network (ITN) of NIAID; recipient of a Research Sponsorship from Nestle; Consultant and Advisory Board Member at Before Brands, Alladapt, IgGenix, NHLBI, and ProBio; and Data and Safety Monitoring Board member at NHLBI. J.L.W., J.N.W., and G.B.S. are employees of Meso Scale Diagnostics (MSD).
Figures










Comment in
-
SARS-CoV-2 vaccination washes away original antigenic sin.Trends Immunol. 2022 Apr;43(4):271-273. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2022.02.009. Epub 2022 Feb 28. Trends Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35272935 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

