Regulation of organelle size and organization during development
- PMID: 35148938
- PMCID: PMC9357868
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.02.002
Regulation of organelle size and organization during development
Abstract
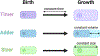
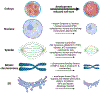
During early embryogenesis, as cells divide in the developing embryo, the size of intracellular organelles generally decreases to scale with the decrease in overall cell size. Organelle size scaling is thought to be important to establish and maintain proper cellular function, and defective scaling may lead to impaired development and disease. However, how the cell regulates organelle size and organization are largely unanswered questions. In this review, we summarize the process of size scaling at both the cell and organelle levels and discuss recently discovered mechanisms that regulate this process during early embryogenesis. In addition, we describe how some recently developed techniques and Xenopus as an animal model can be used to investigate the underlying mechanisms of size regulation and to uncover the significance of proper organelle size scaling and organization.
Keywords: Cell size; Chromosomes; Development; Nucleus; Organelle size; Spindle; Xenopus.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intracellular Scaling Mechanisms.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 Aug 7;7(12):a019067. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a019067. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015. PMID: 26254310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organelle size scaling over embryonic development.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2020 Sep;9(5):e376. doi: 10.1002/wdev.376. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32003549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of Xenopus cell-free extracts to study size regulation of subcellular structures.Int J Dev Biol. 2016;60(7-8-9):277-288. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.160158dl. Int J Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27759156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scaling properties of cell and organelle size.Organogenesis. 2010 Apr-Jun;6(2):88-96. doi: 10.4161/org.6.2.11464. Organogenesis. 2010. PMID: 20885855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitotic spindle scaling during Xenopus development by kif2a and importin α.Elife. 2013 Feb 19;2:e00290. doi: 10.7554/eLife.00290. Elife. 2013. PMID: 23425906 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Conserved nucleocytoplasmic density homeostasis drives cellular organization across eukaryotes.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 15;16(1):7597. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62605-0. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40817332 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Softness Promotes the Metastatic Potential of Large-Nucleated Colorectal Cancer Cells via the ErbB4-Akt1-Lamin A/C Signaling Pathway.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Apr 29;20(7):2748-2762. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.89481. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38725859 Free PMC article.
-
Eukaryotic cell size regulation and its implications for cellular function and dysfunction.Physiol Rev. 2024 Oct 1;104(4):1679-1717. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00046.2023. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Physiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38900644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clustering cell nuclei on microgrooves for disease diagnosis using deep learning.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22476. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05788-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40593025 Free PMC article.
-
Ndc1 drives nuclear pore complex assembly independent of membrane biogenesis to promote nuclear formation and growth.Elife. 2022 Jul 19;11:e75513. doi: 10.7554/eLife.75513. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35852146 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pascual-Carreras E, Marin-Barba M, Herrera-Ubeda C, Font-Martin D, Eckelt K, de Sousa N, Garcia-Fernandez J, Salo E, Adell T, Planarian cell number depends on blitzschnell, a novel gene family that balances cell proliferation and cell death, Development 147(7) (2020) dev184044. - PubMed
-
- Chan CJ, Costanzo M, Ruiz-Herrero T, Monke G, Petrie RJ, Bergert M, Diz-Munoz A, Mahadevan L, Hiiragi T, Hydraulic control of mammalian embryo size and cell fate, Nature 571(7763) (2019) 112–116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

