Exposure to air pollution and risk of incident dementia in the UK Biobank
- PMID: 35149105
- PMCID: PMC8976829
- DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.112895
Exposure to air pollution and risk of incident dementia in the UK Biobank
Abstract
Background: Air pollution may cause inflammatory and oxidative stress damage to the brain, leading to neurodegenerative disease. The association between air pollution and dementia, and modification by apolipoprotein E genotype 4 (APOE-ε4) has yet to be fully investigated.
Objectives: To examine associations of air pollution with three types of incident dementias (Alzheimer's disease (AD), frontotemporal dementia (FTD), and vascular dementia (VAD)), and their potential modification by APOE-ε4 genotype.
Methods: The UK Biobank enrolled >500,000 participants (2006-2010) with ongoing follow-up. We used annual averages of air pollution (PM2.5, PM10, PM2.5-10, PM2.5absorbance, NO2, NOX) for 2010 scaled to interquartile ranges (IQR). We included individuals aged ≥60 years, with no dementia diagnosis prior to January 1, 2010. Time to incident dementia and follow-up time were reported from baseline (January 01, 2010) to last censor event (death, last hospitalization, or loss to follow-up). Cox proportional hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were calculated to estimate the association of air pollutants and incident dementia, and modification of these associations by APOE-ε4.
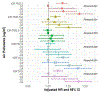
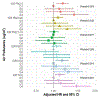
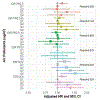
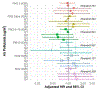
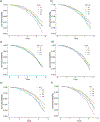
Results: Our sample included 187,194 individuals (including N = 680 AD, N = 377 VAD, N = 63 FTD) with a mean follow-up of 7.04 years. We observed consistent associations of PM2.5 with greater risk of all-cause dementia (HR = 1.17, 95% CI: 1.10, 1.24) and AD (HR = 1.17, 95% CI: 1.06, 1.29). NO2 was also associated with greater risk of any incident dementia (HR = 1.18, 95% CI: 1.10, 1.25), AD (HR = 1.15, 95% CI: 1.04, 1.28) and VAD (HR = 1.18, 95% CI: 1.03, 1.35). APOE-ε4 did not modify the association between any air pollutants and dementia.
Discussion: PM2.5 and NO2 levels were associated with several types of dementia, and these associations were not modified by APOE-ε4. Findings from the UK Biobank support and extend to other epidemiological evidence for the potential association of air pollutants with detrimental brain health during aging.
Keywords: Air pollution; Alzheimer's; Apolipoprotein E4; Dementia; Nitrogen oxides; Particulate matter.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Air pollution, APOE genotype and risk of dementia among individuals with cardiovascular diseases: A population-based longitudinal study.Environ Pollut. 2024 Apr 15;347:123758. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2024.123758. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Environ Pollut. 2024. PMID: 38492747
-
Associations of ambient air pollution exposure and lifestyle factors with incident dementia in the elderly: A prospective study in the UK Biobank.Environ Int. 2024 Aug;190:108870. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2024.108870. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Environ Int. 2024. PMID: 38972114
-
Air Pollution, Genetic Factors, and the Risk of Lung Cancer: A Prospective Study in the UK Biobank.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Oct 1;204(7):817-825. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202011-4063OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 34252012
-
Short-term exposure to particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and ozone (O3) and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Environ Int. 2020 Sep;142:105876. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105876. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Environ Int. 2020. PMID: 32590284
-
Air Pollution and Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Alzheimers Dis. 2020;77(2):701-714. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200483. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020. PMID: 32741830
Cited by
-
Common Fatal Neurodegenerative Diseases Revisited: Beyond Age, Comorbidities, and Devastating Terminal Neuropathology There Is Hope With Prevention.Front Neurol. 2022 May 11;13:901447. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.901447. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35645968 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Air pollution: a latent key driving force of dementia.BMC Public Health. 2024 Sep 2;24(1):2370. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19918-4. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39223534 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological repercussions of PM air pollution in human aging: a comprehensive review of urban and rural environments.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 17;16:1517090. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1517090. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40034819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Air Pollution as an Environmental Risk Factor for Alzheimer's Disease and Related Dementias.Med Res Arch. 2024 Oct;12(10):5825. doi: 10.18103/mra.v12i10.5825. Epub 2024 Oct 31. Med Res Arch. 2024. PMID: 39822906 Free PMC article.
-
APOE ε4-independent pathways predominate in the association between retinal nerve fiber layer thinning and 12-year incident dementia.Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2025 May 29;11(2):e70104. doi: 10.1002/trc2.70104. eCollection 2025 Apr-Jun. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2025. PMID: 40453978 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beelen R, Hoek G, Vienneau D, Eeftens M, Dimakopoulou K, Pedeli X, et al. 2013. Development of no2 and nox land use regression models for estimating air pollution exposure in 36 study areas in europe - the ESCAPE project. Atmos Environ 72:10–23, 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.02.037. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

