Systemic lupus erythematosus as a genetic disease
- PMID: 35149194
- PMCID: PMC9167620
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2022.108953
Systemic lupus erythematosus as a genetic disease
Abstract
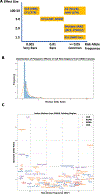
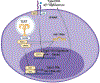
Systemic lupus erythematosus is the prototypical systemic autoimmune disease, as it is characterized both by protean multi-organ system manifestations and by the uniform presence of pathogenic autoantibodies directed against components of the nucleus. Prior to the modern genetic era, the diverse clinical manifestations of SLE suggested to many that SLE patients were unlikely to share a common genetic risk basis. However, modern genetic studies have revealed that SLE usually arises when an environmental exposure occurs in an individual with a collection of genetic risk variants passing a liability threshold. Here, we summarize the current state of the field aimed at: (1) understanding the genetic architecture of this complex disease, (2) synthesizing how this genetic risk architecture impacts cellular and molecular disease pathophysiology, (3) providing illustrative examples that highlight the rich complexity of the pathobiology of this prototypical autoimmune disease and (4) communicating this complex etiopathogenesis to patients.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

