DS-7300a, a DNA Topoisomerase I Inhibitor, DXd-Based Antibody-Drug Conjugate Targeting B7-H3, Exerts Potent Antitumor Activities in Preclinical Models
- PMID: 35149548
- PMCID: PMC9377751
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-21-0554
DS-7300a, a DNA Topoisomerase I Inhibitor, DXd-Based Antibody-Drug Conjugate Targeting B7-H3, Exerts Potent Antitumor Activities in Preclinical Models
Abstract
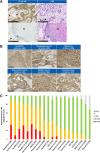
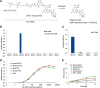
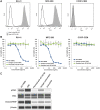
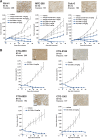
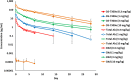
B7-H3 is overexpressed in various solid tumors and has been considered as an attractive target for cancer therapy. Here, we report the development of DS-7300a, a novel B7-H3-targeting antibody-drug conjugate with a potent DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor, and its in vitro profile, pharmacokinetic profiles, safety profiles, and in vivo antitumor activities in nonclinical species. The target specificity and species cross-reactivity of DS-7300a were assessed. Its pharmacologic activities were evaluated in several human cancer cell lines in vitro and xenograft mouse models, including patient-derived xenograft (PDX) mouse models in vivo. Pharmacokinetics was investigated in cynomolgus monkeys. Safety profiles in rats and cynomolgus monkeys were also assessed. DS-7300a specifically bound to B7-H3 and inhibited the growth of B7-H3-expressing cancer cells, but not that of B7-H3-negative cancer cells, in vitro. Additionally, treatment with DS-7300a and DXd induced phosphorylated checkpoint kinase 1, a DNA damage marker, and cleaved PARP, an apoptosis marker, in cancer cells. Moreover, DS-7300a demonstrated potent in vivo antitumor activities in high-B7-H3 tumor xenograft models, including various tumor types of high-B7-H3 PDX models. Furthermore, DS-7300a was stable in circulation with acceptable pharmacokinetic profiles in monkeys, and well tolerated in rats and monkeys. DS-7300a exerted potent antitumor activities against B7-H3-expressing tumors in in vitro and in vivo models, including PDX mouse models, and showed acceptable pharmacokinetic and safety profiles in nonclinical species. Therefore, DS-7300a may be effective in treating patients with B7-H3-expressing solid tumors in a clinical setting.
©2022 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
References
-
- Chapoval AI, Ni J, Lau JS, Wilcox RA, Flies DB, Liu D, et al. . B7-H3: a costimulatory molecule for T cell activation and IFN-γ production. Nat Immunol 2001;2:269–74. - PubMed
-
- Sun M, Richards S, Prasad DVR, Mai XM, Rudensky A, Dong C. Characterization of mouse and human B7-H3 genes. J Immunol 2002;168:6294–7. - PubMed
-
- Ling V, Wu PW, Spaulding V, Kieleczawa J, Luxenberg D, Carreno BM, et al. . Duplication of primate and rodent B7-H3 immunoglobulin V- and C-like domains: divergent history of functional redundancy and exon loss. Genomics 2003;82:365–77. - PubMed
-
- Steinberger P, Majdic O, Derdak SV, Pfistershammer K, Kirchberger S, Klauser C, et al. . Molecular characterization of human 4Ig-B7-H3, a member of the B7 family with four Ig-like domains. J Immunol 2004;172:2352–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

