RYBP regulates Pax6 during in vitro neural differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 35149723
- PMCID: PMC8837790
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-06228-1
RYBP regulates Pax6 during in vitro neural differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells
Abstract
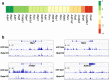
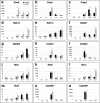
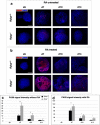
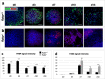
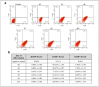
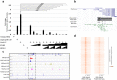
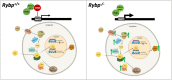
We have previously reported that RING1 and YY1 binding protein (RYBP) is important for central nervous system development in mice and that Rybp null mutant (Rybp-/-) mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells form more progenitors and less terminally differentiated neural cells than the wild type cells in vitro. Accelerated progenitor formation coincided with a high level of Pax6 expression in the Rybp-/- neural cultures. Since Pax6 is a retinoic acid (RA) inducible gene, we have analyzed whether altered RA signaling contributes to the accelerated progenitor formation and impaired differentiation ability of the Rybp-/- cells. Results suggested that elevated Pax6 expression was driven by the increased activity of the RA signaling pathway in the Rybp-/- neural cultures. RYBP was able to repress Pax6 through its P1 promoter. The repression was further attenuated when RING1, a core member of ncPRC1s was also present. According to this, RYBP and PAX6 were rarely localized in the same wild type cells during in vitro neural differentiation. These results suggest polycomb dependent regulation of Pax6 by RYBP during in vitro neural differentiation. Our results thus provide novel insights on the dynamic regulation of Pax6 and RA signaling by RYBP during mouse neural development.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Tonge PD, Andrews PW. Retinoic acid directs neuronal differentiation of human pluripotent stem cell lines in a non-cell-autonomous manner. Differ. Res. Biol. Divers. 2010;80:20–30. - PubMed
-
- Gajović S, St-Onge L, Yokota Y, Gruss P. Retinoic acid mediates Pax6 expression during in vitro differentiation of embryonic stem cells. Differ. Res. Biol. Divers. 1997;62:187–192. - PubMed
-
- Rhinn M, Dollé P. Retinoic acid signalling during development. Development. 2012;139:843–858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

