Randomised phase II trial of weekly ixabepilone ± biweekly bevacizumab for platinum-resistant or refractory ovarian/fallopian tube/primary peritoneal cancer
- PMID: 35149854
- PMCID: PMC8853032
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-022-01717-6
Randomised phase II trial of weekly ixabepilone ± biweekly bevacizumab for platinum-resistant or refractory ovarian/fallopian tube/primary peritoneal cancer
Erratum in
-
Correction: Randomised phase II trial of weekly ixabepilone ± biweekly bevacizumab for platinum-resistant or refractory ovarian/fallopian tube/primary peritoneal cancer.Br J Cancer. 2024 Apr;130(6):1073. doi: 10.1038/s41416-024-02628-4. Br J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38438590 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: This multi-center RP2 study assessed activity/safety of ixabepilone + bevacizumab compared to ixabepilone in platinum-resistant/refractory ovarian/fallopian tube/primary peritoneal cancer. Additional objectives were to examine the role of prior bevacizumab and taxanes, and explore class III-ß-tubulin (TUBB3) as a predictive biomarker.
Methods: Participants were randomised to receive ixabepilone 20 mg/m2 days 1, 8, 15 with (IXA + BEV) or without (IXA) bevacizumab 10 mg/kg days 1, 15 every 28 days. Patients were stratified by prior BEV. The primary endpoint was PFS. OS, safety, and ORR served as secondary endpoints.
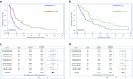
Results: Among 76 evaluable patients who received IXA + BEV (n = 39) compared to IXA (n = 37), the ORR was 33% (n = 13) versus 8% (n = 3)(P = 0.004), durable at 6 months in 37% (n = 14) and 3% (n = 1) (P < 0.001). BEV significantly improved PFS (median:5.5 vs 2.2 months, HR = 0.33, 95%CI 0.19-0.55, P < 0.001) and OS (median:10.0 vs 6.0 months, HR = 0.52, 95%CI 0.31-0.87, P = 0.006). Both regimens were well-tolerated. TUBB3 expression did not predict response. Subgroup analyses revealed minimal effect of prior BEV or taxane resistant/refractory status on response to IXA + BEV.
Conclusions: IXA + BEV is a well-tolerated, effective combination for platinum/taxane-resistant ovarian cancer that extends PFS and likely OS relative to IXA monotherapy. Prior receipt of BEV should not preclude the use of IXA + BEV. TUBB3 is not a predictive biomarker.
Clinical trial registration: NCT3093155.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03093155.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Wysham WZ, Schaffer EM, Coles T, Roque DR, Wheeler SB, Kim KH. Adding bevacizumab to single agent chemotherapy for the treatment of platinum-resistant recurrent ovarian cancer: a cost effectiveness analysis of the AURELIA trial. Gynecol Oncol. 2017;145:340–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2017.02.039. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

