Molecular Identification of Nocardia seriolae and Comparative Analysis of Spleen Transcriptomes of Hybrid Snakehead (Channa maculata Female × Channa argus Male) With Nocardiosis Disease
- PMID: 35154103
- PMCID: PMC8828968
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.778915
Molecular Identification of Nocardia seriolae and Comparative Analysis of Spleen Transcriptomes of Hybrid Snakehead (Channa maculata Female × Channa argus Male) With Nocardiosis Disease
Abstract
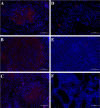
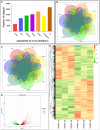
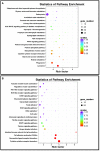
Hybrid snakehead (Channa maculata female × Channa argus male) is a new freshwater aquaculture fish species in southern China. During intensive aquaculture, hybrid snakeheads are often infected by Nocardia seriolae. In this study, hybrid snakehead infected suspiciously by N. seriolae in an artificial breeding pond were examined. Diseased hybrid snakeheads swam slowly without food intake, and the clinical symptoms included skin wound, anal swelling and ascites, and white granulomatous in liver, spleen, and kidney of fish. Through bacterial isolation, 16S rDNA sequencing, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and artificial infection experiment, the pathogen was identified as N. seriolae. Furthermore, the spleen samples from diseased and healthy male hybrid snakeheads in the same pond were used for RNA-Seq analysis. A total of 3,512 unique transcripts (unigenes) were identified as differentially expressed genes (DEGs), and 1,886 of them were up-regulated in diseased fish. The expression patterns of 20 DEGs were verified by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). Several immune-related pathways and many immune-related genes were identified. qPCR results showed that the expression patterns of immune-related genes in the liver and kidney of diseased fish were comparable to that in the spleen. This study provides deep-sequencing data of hybrid snakehead spleen and will help understand the immune response of hybrid snakehead to N. seriolae. It is also helpful for the biomarker screening of fish-borne Nocardia spp. and the breeding of nocardiosis-resistant fish species.
Keywords: Nocardia seriolae; RNA-seq; fish; hybrid snakehead; immune response.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Zhang, Dong and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
Author HZ is employed by Zhongshan Ronghai aquaculture Co. Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Zhao PF, Li FJ, Chen XR, Chen YJ, Lin SM, Zhang L, et al. Dietary Lipid Concentrations Influence Growth, Liver Oxidative Stress, and Serum Metabolites of Juvenile Hybrid Snakehead (Channa Argus X Channa Maculata). Aquacult Int (2016) 24:1353–64. doi: 10.1007/s10499-016-9993-0 - DOI
-
- Zhou LG, Feng XY, Wang YX, Liu XY, Guo SR, Chen FD. Comparative Study on Flesh Quality of Hybrid Snakehead (Channa Maculate ♀×Channa Argus♂) and Channa Argus . J Shanghai Ocean University (2011) 20:303–7. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0b013e3181f49ac7 - DOI
-
- Zhang YF, Sun ZZ, Wang AL, Ye CX, Zhu X. Effects of Dietary Protein and Lipid Levels on Growth, Body and Plasma Biochemical Composition and Selective Gene Expression in Liver of Hybrid Snakehead (Channa Maculata Female X Channa Argus Male) Fingerlings. Aquaculture (2017) 468:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.09.052 - DOI
-
- Que TT, Zheng JW, Chen SG, Jiang QQ, Liu WJ, Ye XQ, et al. Effect of Super-Chilling and Frozen on the Meat Quality of Snakehead. J Chin Institute Food Sci Technol (2015) 15:136–47. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2015.06.019 - DOI
-
- Chen JL, Li YQ, Wang WJ, Xia LQ, Wang ZW, Hou SY, et al. Transcriptome Analysis of Immune-Related Gene Expression in Hybrid Snakehead (Channa Maculata Female X Channa Argus Male) After Challenge With Nocardia Seriolae . Fish Shellfish Immun (2018) 81:476–84. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.04.113 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

