Role of ROS-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in the Formation of Calcium Oxalate Nephrolithiasis
- PMID: 35154136
- PMCID: PMC8828488
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.818625
Role of ROS-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in the Formation of Calcium Oxalate Nephrolithiasis
Abstract
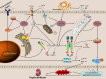
Calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis is a common and highly recurrent disease in urology; however, its precise pathogenesis is still unknown. Recent research has shown that renal inflammatory injury as a result of the cell-crystal reaction plays a crucial role in the development of calcium oxalate kidney stones. An increasing amount of research have confirmed that inflammation mediated by the cell-crystal reaction can lead to inflammatory injury of renal cells, promote the intracellular expression of NADPH oxidase, induce extensive production of reactive oxygen species, activate NLRP3 inflammasome, discharge a great number of inflammatory factors, trigger inflammatory cascading reactions, promote the aggregation, nucleation and growth process of calcium salt crystals, and ultimately lead to the development of intrarenal crystals and even stones. The renal tubular epithelial cells (RTECs)-crystal reaction, macrophage-crystal reaction, calcifying nanoparticles, endoplasmic reticulum stress, autophagy activation, and other regulatory factors and mechanisms are involved in this process.
Keywords: autophagy; endoplasmic reticulum stress; inflammasome; macrophage; nanoparticles; reactive oxygen species.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Sun, Kang, He, Liu, Wu, Li, Wang, Tao, Guan, She, Xu and Deng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

