Genetic Parameter Estimation and Genome-Wide Association Study-Based Loci Identification of Milk-Related Traits in Chinese Holstein
- PMID: 35154251
- PMCID: PMC8836289
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.799664
Genetic Parameter Estimation and Genome-Wide Association Study-Based Loci Identification of Milk-Related Traits in Chinese Holstein
Abstract
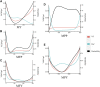
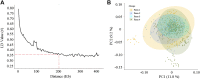
Accurately estimating the genetic parameters and revealing more genetic variants underlying milk production and quality are conducive to the genetic improvement of dairy cows. In this study, we estimate the genetic parameters of five milk-related traits of cows-namely, milk yield (MY), milk fat percentage (MFP), milk fat yield (MFY), milk protein percentage (MPP), and milk protein yield (MPY)-based on a random regression test-day model. A total of 95,375 test-day records of 9,834 cows in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River were used for the estimation. In addition, genome-wide association studies (GWASs) for these traits were conducted, based on adjusted phenotypes. The heritability, as well as the standard errors, of MY, MFP, MFY, MPP, and MPY during lactation ranged from 0.22 ± 0.02 to 0.31 ± 0.04, 0.06 ± 0.02 to 0.15 ± 0.03, 0.09 ± 0.02 to 0.28 ± 0.04, 0.07 ± 0.01 to 0.16 ± 0.03, and 0.14 ± 0.02 to 0.27 ± 0.03, respectively, and the genetic correlations between different days in milk (DIM) within lactations decreased as the time interval increased. Two, six, four, six, and three single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were detected, which explained 5.44, 12.39, 8.89, 10.65, and 7.09% of the phenotypic variation in MY, MFP, MFY, MPP, and MPY, respectively. Ten Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways and 25 Gene Ontology terms were enriched by analyzing the nearest genes and genes within 200 kb of the detected SNPs. Moreover, 17 genes in the enrichment results that may play roles in milk production and quality were selected as candidates, including CAMK2G, WNT3A, WNT9A, PLCB4, SMAD9, PLA2G4A, ARF1, OPLAH, MGST1, CLIP1, DGAT1, PRMT6, VPS28, HSF1, MAF1, TMEM98, and F7. We hope that this study will provide useful information for in-depth understanding of the genetic architecture of milk production and quality traits, as well as contribute to the genomic selection work of dairy cows in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River.
Keywords: Chinese holstein; genetic parameters; genome-wide association study (GWAS); milk-related traits; test-day model.
Copyright © 2022 Lu, Arbab, Abdalla, Liu, Zhang, Xu, Su and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genome-Wide Association Study of Lactation Traits in Chinese Holstein Cows in Southern China.Animals (Basel). 2023 Aug 7;13(15):2545. doi: 10.3390/ani13152545. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37570353 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic parameters and genome-wide association for milk production traits and somatic cell score in different lactation stages of Shanghai Holstein population.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 5;13:940650. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.940650. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36134029 Free PMC article.
-
Descriptive Statistics and Genome-Wide Copy Number Analysis of Milk Production Traits of Jiangsu Chinese Holstein Cows.Animals (Basel). 2023 Dec 19;14(1):17. doi: 10.3390/ani14010017. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38200748 Free PMC article.
-
Short communication: Replication of genome-wide association studies for milk production traits in Chinese Holstein by an efficient rotated linear mixed model.J Dairy Sci. 2019 Mar;102(3):2378-2383. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-15298. Epub 2019 Jan 11. J Dairy Sci. 2019. PMID: 30639022
-
Single-step genome-wide association analyses for milk urea concentration in Walloon Holstein cows.J Dairy Sci. 2024 May;107(5):3020-3031. doi: 10.3168/jds.2023-23902. Epub 2023 Dec 4. J Dairy Sci. 2024. PMID: 38056570
Cited by
-
Genomic Regions and Candidate Genes Associated with Milk Production Traits in Holstein and Its Crossbred Cattle: A Review.Int J Genomics. 2023 Jul 27;2023:8497453. doi: 10.1155/2023/8497453. eCollection 2023. Int J Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37547753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Trends in Food Quality and Authentication: The Role of Omics Technologies in Dairy and Meat Production.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 6;26(9):4405. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094405. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiscale Entropy-Based Feature Extraction for the Detection of Instability Inception in Axial Compressors.Entropy (Basel). 2024 Jan 2;26(1):48. doi: 10.3390/e26010048. Entropy (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38248174 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Association Study of Lactation Traits in Chinese Holstein Cows in Southern China.Animals (Basel). 2023 Aug 7;13(15):2545. doi: 10.3390/ani13152545. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37570353 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Marker-Assisted Selection of ABCG2, CD44, SPP1 Genes Contribute to Milk Production Traits of Chinese Holstein.Animals (Basel). 2022 Dec 26;13(1):89. doi: 10.3390/ani13010089. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36611698 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bertolini F., Schiavo G., Bovo S., Sardina M. T., Mastrangelo S., Dall’Olio S., et al. (2020). Comparative Selection Signature Analyses Identify Genomic Footprints in Reggiana Cattle, the Traditional Breed of the Parmigiano-Reggiano Cheese Production System. Animal 14 (5), 921–932. 10.1017/S1751731119003318 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bignardi A. B., El Faro L., Cardoso V. L., Machado P. F., de Albuquerque L. G. (2009b). Random Regression Models to Estimate Test-Day Milk Yield Genetic Parameters Holstein Cows in Southeastern Brazil. Livestock Sci. 123 (1), 1–7. 10.1016/j.livsci.2008.09.021 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

