Homologous Cloning of Potassium Channel Genes From the Superior Apple Rootstock Line 12-2, Which is Tolerant to Apple Replant Disease
- PMID: 35154275
- PMCID: PMC8826240
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.803160
Homologous Cloning of Potassium Channel Genes From the Superior Apple Rootstock Line 12-2, Which is Tolerant to Apple Replant Disease
Abstract
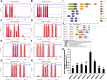
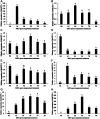
Potassium channels are important ion channels that are responsible for the absorption of potassium in the plant nutrient uptake system. In this study, we used homologous molecular cloning to obtain 8 K+ channel genes from the superior apple rootstock line 12-2 (self-named): MsAKT1-1, MsKAT3-2, MsKAT1-3, MsK2P3-4, MsK2P3-5, MsK2P5-6, MsK2P3-7, and MsK2P3-8. Their lengths varied from 942 bp (MsK2P5-6) to 2625 bp (MsAKT1-1), and the number of encoded amino acids varied from 314 (MsK2P5-6) to 874 (MsAKT1-1). Subcellular localization predictions showed that MsAKT1-1, MsKAT3-2, and MsKAT1-3 were localized on the plasma membrane, and MsK2P3-4, MsK2P3-5, MsK2P5-6, MsK2P3-7, and MsK2P3-8 were localized on the vacuole and plasma membrane. The 8 K+ channel proteins contained α helices, extended strands, β turns, and random coils. MsKAT1-3 had four transmembrane structures, MsKAT3-2 had six, and the other six K+ channel genes had five. Protein structure domain analysis showed that MsAKT1-1 contained nine protein domains, followed by MsKAT3-2 with four, MsKAT1-3 with three, and the other five two-pore domain K+ channel proteins with two. Semi-quantitative RT-PCR detection of the K+ channel genes showed that their expression levels were high in roots. qRT-PCR analysis showed that the relative expression levels of the 8 genes changed after exposure to ARD stress. The above results provide a theoretical basis for further research on the functions of potassium channel genes in 12-2 and a scientific basis for the breeding of ARD-resistant rootstock.
Keywords: ARD-resistant rootstock; K+ channel genes; apple replant disease; biochemical information; homologous molecular cloning.
Copyright © 2022 Mao, Yin, Cui, Wang, Su, Qin, Liu, Hu and Shen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detection of Root Physiological Parameters and Potassium and Calcium Currents in the Rhizoplane of the Apple Rootstock Superior Line 12-2 With Improved Apple Replant Disease Resistance.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Dec 17;12:734430. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.734430. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34975935 Free PMC article.
-
Inter-row cropping and rootstock genotype selection in a UK cider orchard to combat apple replant disease.Phytopathol Res. 2023;5(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s42483-023-00184-y. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Phytopathol Res. 2023. PMID: 38800641 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Candidate Genes Associated With Tolerance to Apple Replant Disease by Genome-Wide Transcriptome Analysis.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 9;13:888908. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.888908. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35615498 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the molecular responses of apple rootstock resistant to ARD pathogens: challenges and opportunities for development of genomics-assisted breeding tools.Hortic Res. 2014 Aug 20;1:14043. doi: 10.1038/hortres.2014.43. eCollection 2014. Hortic Res. 2014. PMID: 26504547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging issues of connexin channels: biophysics fills the gap.Q Rev Biophys. 2001 Aug;34(3):325-472. doi: 10.1017/s0033583501003705. Q Rev Biophys. 2001. PMID: 11838236 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

