Preferential radiosensitization to glioblastoma cancer stem cell-like cells by a Hsp90 inhibitor, N-vinylpyrrolidone-AUY922
- PMID: 35154433
- PMCID: PMC8822487
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2022.13222
Preferential radiosensitization to glioblastoma cancer stem cell-like cells by a Hsp90 inhibitor, N-vinylpyrrolidone-AUY922
Abstract
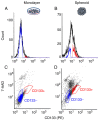
The present study examined the radiosensitization induced by a heat shock protein 90 inhibitor, N-vinylpyrrolidone (NVP)-AUY922, in CD133-positive cells in a hypoxic area of T98G spheroids. CD133-positive cells that are induced in the hypoxic microenvironment of spheroids have previously been reported to exhibit cancer stem cell-like properties. The present study used CD133-positive cells from a glioblastoma cell line (T98G) as cancer stem cell-like cells. CD133-positive and negative cells were sorted from T98G spheroids using fluorescence-activated cell sorting and used for colony formation assay. Colony formation assay results indicated that NVP-AUY922 enhanced radiosensitivity more strongly in CD133-positive cells compared with CD133-negative cells. This result showed that NVP-AUY922 was a preferential radiosensitization candidate targeting glioblastoma cancer stem cells. The mechanisms underlying radiosensitization by NVP-AUY922 are discussed in relation to the properties of cancer stem cells. Overall, HIF-1α inhibition by NVP-AUY922 may induce higher sensitization of cancer stem cells to radiation.
Keywords: N-vinylpyrrolidone-AUY922; cancer stem cell; glioblastoma; heat shock protein 90 inhibitor; radiosensitization.
Copyright: © Tani et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B, Belanger K, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:459–466. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70025-7. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
