Investigating changes of proteome in the bovine milk serum after retort processing using proteomics techniques
- PMID: 35154669
- PMCID: PMC8825719
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.2300
Investigating changes of proteome in the bovine milk serum after retort processing using proteomics techniques
Abstract
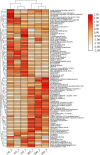
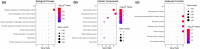
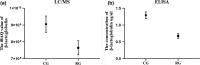
The objective of this study was to investigate the changes of the proteins in bovine milk serum after retort processing by label-free quantification proteomics techniques. A total of 96 and 106 proteins were quantified in control group (CG) and retort group (RG), respectively. Hierarchical clustering analysis of the identified milk serum proteins showed a decrease in the abundance of most proteins, such as serum albumin, lactoperoxidase, lactotransferrin, and complement C3, and an increase in the abundance of other proteins such as κ-casein, lipocalin 2, and Perilipin. Student's t-test showed 21 proteins significantly differential abundance between CG and RG (p < .05), of which intensity-based absolute quantification (iBAQ) of five proteins decreased and iBAQ of 16 proteins increased. Bioinformatics analysis demonstrated that retort processing increased the digestibility of proteins, but this improvement was offset by a decrease in the digestibility of proteins caused by protein modification. Our results provide insight into the proteome of retort sterilized milk for the first time. Given the extremely high security of retort sterilized milk, the proteome of bovine milk serum changes after retort sterilization exposed in this study will contribute to the formula design of retort sterilized milk products.
Keywords: LFQ; bioinformatics; bovine milk; proteomics; retort sterilized milk.
© 2021 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of the bovine milk proteome in early-lactation Holstein and Jersey breeds of dairy cows.J Proteomics. 2016 Jan 1;130:200-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2015.09.024. Epub 2015 Sep 21. J Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 26391770 Free PMC article.
-
Composition and Variation of Macronutrients, Immune Proteins, and Human Milk Oligosaccharides in Human Milk From Nonprofit and Commercial Milk Banks.J Hum Lact. 2018 Feb;34(1):120-129. doi: 10.1177/0890334417710635. Epub 2017 Jun 14. J Hum Lact. 2018. PMID: 28614672
-
A novel proteomic approach for the identification and relative quantification of disulfide-bridges in the human milk proteome.J Proteomics. 2024 Jun 15;301:105194. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2024.105194. Epub 2024 May 7. J Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 38723850
-
Review: Proteomic approaches to control lactational parameters in dairy cows.Animal. 2019 Jul;13(S1):s82-s85. doi: 10.1017/S1751731118003476. Animal. 2019. PMID: 31280743 Review.
-
The proteomic advantage: label-free quantification of proteins expressed in bovine milk during experimentally induced coliform mastitis.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2010 Dec 15;138(4):252-66. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2010.10.004. Epub 2010 Oct 14. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2010. PMID: 21067814 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of spray drying and freeze drying on the protein profile of whey protein concentrate.J Food Sci. 2024 Nov;89(11):7477-7493. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.17349. Epub 2024 Oct 4. J Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 39366780
-
Effects of Different Processing on miRNA and Protein in Small Extracellular Vesicles of Goat Dairy Products.Nutrients. 2024 Dec 16;16(24):4331. doi: 10.3390/nu16244331. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39770952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, D. , Gonzalez‐Duarte, A. , O’Riordan, W. D. , Yang, C.‐C. , Ueda, M. , Kristen, A. V. , Tournev, I. , Schmidt, H. H. , Coelho, T. , Berk, J. L. , Lin, K.‐P. , Vita, G. , Attarian, S. , Planté‐Bordeneuve, V. , Mezei, M. M. , Campistol, J. M. , Buades, J. , Brannagan, T. H. , Kim, B. J. , Suhr, O. B. (2018). Patisiran, an RNAi therapeutic, for hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. New England Journal of Medicine, 379(1), 11–21. 10.1056/NEJMoa1716153 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Almughlliq, F. B. , Koh, Y. Q. , Peiris, H. N. , Vaswani, K. , Holland, O. , Meier, S. , Roche, J. R. , Burke, C. R. , Crookenden, M. A. , Arachchige, B. J. , Reed, S. , & Mitchell, M. D. (2019). Circulating exosomes may identify biomarkers for cows at risk for metabolic dysfunction. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 13879. 10.1038/s41598-019-50244-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anagnostopoulos, A. K. , Katsafadou, A. I. , Pierros, V. , Kontopodis, E. , Fthenakis, G. C. , Arsenos, G. , Karkabounas, S. C. , Tzora, A. , Skoufos, I. , & Tsangaris, G. T. (2016). Milk of Greek sheep and goat breeds; characterization by means of proteomics. Journal of Proteomics, 147(1), 76–84. 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.04.008 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

