Physicochemical Changes of Contaminated Titanium Discs Treated With Erbium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (Er:YAG) Laser Irradiation or Air-Flow Abrasion: An In Vitro Study
- PMID: 35155152
- PMCID: PMC8837866
- DOI: 10.34172/jlms.2021.67
Physicochemical Changes of Contaminated Titanium Discs Treated With Erbium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (Er:YAG) Laser Irradiation or Air-Flow Abrasion: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
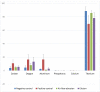
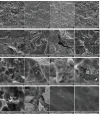
Introduction: Peri-implantitis is a common complication of dental implant treatment. A cause-and-effect relationship has been previously documented between microbial plaque and peri-implantitis and implant failure. A difference has been reported in the disinfection efficacy of erbium laser irradiation and air-flow abrasion for contaminated titanium surfaces. Also, the surface changes caused by lasers and air-flow abrasion have not been well studied. Thus, the purpose of this study was to compare the surface changes of contaminated titanium discs following decontamination by erbium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Er:YAG) laser irradiation and air-flow abrasion. Methods: Twenty-eight intact, sandblasted, and acid-etched (SLA) titanium discs were used. Twenty-four titanium discs were contaminated with Escherichia coli. Then, they were decontaminated by using Er:YAG laser irradiation and air-flow abrasion. Four discs remained intact. The mean and standard deviation of the contact angle and the weight percentage of aluminum, titanium, oxygen, carbon, phosphorus, and calcium were measured. Qualitative changes in surface topography of titanium discs were assessed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Results: The mean weight percentage of carbon in the air-flow abrasion group (4.98%) experienced a significant reduction compared with the contaminated (positive control) group (P=0.035). The contact angles were 46.54° and 38.67° in the laser and air-flow abrasion groups respectively, which were significantly lower than the value in the positive control group (75.15°) (P ≤0.001). SEM micrographs showed no significant change in the surface area in either technique. Conclusion: Air-flow abrasion was more successful in improving the surface characteristics of titanium discs with no alteration in surface topography or elements, compared with Er:YAG laser irradiation. Further studies regarding the safety of the Er:YAG laser for the decontamination of titanium surfaces are recommended.
Keywords: Decontamination; Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy; Lasers; Peri-Implantitis; SEM; Wettability.
Copyright © 2021 J Lasers Med Sci.
References
-
- Mombelli A. Etiology, diagnosis, and treatment considerations in Peri-Implantitis. Curr opin Periodontol. 1997;4:127–36. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources