Exosomes in Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 35155236
- PMCID: PMC8828506
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.793432
Exosomes in Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
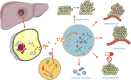
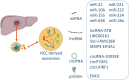
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles with a diameter of 30-150 nm that are released by most types of cells and have been confirmed to be involved in many physical and pathological processes, especially in cell to cell communication. Compared with other vesicles, exosomes have a unique double-layer saclike structure that allows them to be present stably in various body fluids, including blood, cerebrospinal fluid, urine, saliva, and serous cavity effusion. The cargoes of exosomes reflect the characteristics of host cells. Due to the nature of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells, heterogeneity in the bioactive substances usually exist in exosomes. In addition, exosomes can efficiently deliver cargoes to the target cells to exert pathological functions, playing important role in tumor occurrence, development, metastasis, immune regulation, and drug resistance. Previous studies have been shown that exosomes have wide applications in diagnosis and treatment of HCC. In this review, we discuss these recent findings and highlight the significant roles of exosomes in HCC, focusing on the effect and underlying mechanisms of exosomes to regulate HCC progression and the potential clinical value of exosomes as biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Keywords: angiogenesis; biomarker; drug resistance; exosomes; hepatocellular carcinoma; metastasis.
Copyright © 2022 Li and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exosomes in head and neck cancer: Roles, mechanisms and applications.Cancer Lett. 2020 Dec 1;494:7-16. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.07.005. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 32781015 Review.
-
Exosome in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: an update.J Cancer. 2021 Mar 5;12(9):2526-2536. doi: 10.7150/jca.54566. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33854614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Perspectives on the Unique Roles of Exosomes in Drug Resistance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2022 Feb 18;9:99-112. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S351038. eCollection 2022. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2022. PMID: 35211428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of exosomes in hepatocellular carcinoma and the regulation of traditional Chinese medicine.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 17;14:1110922. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1110922. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36733504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes as potent regulators of HCC malignancy and potential bio-tools in clinical application.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Oct 15;8(10):17088-95. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26770301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cathelicidin Antimicrobial Peptide Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 27;24(21):15652. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115652. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958632 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Interplay of Apoptosis and Autophagy.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 13;11(4):1166. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041166. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A prognostic exosome-related LncRNA risk model correlates with the immune microenvironment in liver cancer.Front Genet. 2022 Aug 23;13:965329. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.965329. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36081999 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes-mediated crosstalk between glioma and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023 Aug;29(8):2074-2085. doi: 10.1111/cns.14239. Epub 2023 May 11. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023. PMID: 37170647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-Invasive Biomarkers for Immunotherapy in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 23;14(19):4631. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194631. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230554 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

