Stromal Fibroblasts Counteract the Caveolin-1-Dependent Radiation Response of LNCaP Prostate Carcinoma Cells
- PMID: 35155239
- PMCID: PMC8826751
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.802482
Stromal Fibroblasts Counteract the Caveolin-1-Dependent Radiation Response of LNCaP Prostate Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
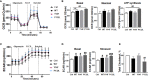
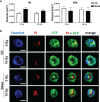
In prostate cancer (PCa), a characteristic stromal-epithelial redistribution of the membrane protein caveolin 1 (CAV1) occurs upon tumor progression, where a gain of CAV1 in the malignant epithelial cells is accompanied by a loss of CAV1 in the tumor stroma, both facts that were correlated with higher Gleason scores, poor prognosis, and pronounced resistance to therapy particularly to radiotherapy (RT). However, it needs to be clarified whether inhibiting the CAV1 gain in the malignant prostate epithelium or limiting the loss of stromal CAV1 would be the better choice for improving PCa therapy, particularly for improving the response to RT; or whether ideally both processes need to be targeted. Concerning the first assumption, we investigated the RT response of LNCaP PCa cells following overexpression of different CAV1 mutants. While CAV1 overexpression generally caused an increased epithelial-to-mesenchymal phenotype in respective LNCaP cells, effects that were accompanied by increasing levels of the 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a master regulator of cellular homeostasis, only wildtype CAV1 was able to increase the three-dimensional growth of LNCaP spheroids, particularly following RT. Both effects could be limited by an additional treatment with the SRC inhibitor dasatinib, finally resulting in radiosensitization. Using co-cultured (CAV1-expressing) fibroblasts as an approximation to the in vivo situation of early PCa it could be revealed that RT itself caused an activated, more tumor-promoting phenotype of stromal fibroblats with an increased an increased metabolic potential, that could not be limited by combined dasatinib treatment. Thus, targeting fibroblasts and/or limiting fibroblast activation, potentially by limiting the loss of stromal CAV1 seems to be absolute for inhibiting the resistance-promoting CAV1-dependent signals of the tumor stroma.
Keywords: SRC; caveolin-1; dasatinib; fibroblast; prostate cancer; radiotherapy; therapy resistance; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2022 Wittka, Ketteler, Borgards, Maier, Herskind, Jendrossek and Klein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

