Xpert Bladder Cancer Monitor May Avoid Cystoscopies in Patients Under "Active Surveillance" for Recurrent Bladder Cancer (BIAS Project): Longitudinal Cohort Study
- PMID: 35155263
- PMCID: PMC8830778
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.832835
Xpert Bladder Cancer Monitor May Avoid Cystoscopies in Patients Under "Active Surveillance" for Recurrent Bladder Cancer (BIAS Project): Longitudinal Cohort Study
Abstract
Objectives: To test the hypothesis that patients under active surveillance (AS) for Non-muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer (NMIBC) who were negative on longitudinal re-testing by the Xpert® Bladder Cancer Monitor (Xpert BC Monitor) assay may avoid unnecessary cystoscopies and urine cytology (UC).
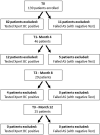
Subjects/patients or materials and methods: This is a prospective cohort study of patients enrolled in the AS protocol for recurrent NMIBC (Bladder Cancer Italian Active Surveillance, BIAS project), whose urine samples were analyzed by Xpert BC Monitor upon entry in the study (T0). Patients who had a negative Xpert test and did not fail AS, underwent additional Xpert tests after 4 (T1), 8 (T2), and 12 (T3) months. The clinical utility of Xpert was assessed by determining the number of cystoscopies and UC that could be avoided within 1 year.
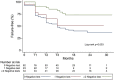
Results: Overall, 139 patients were tested with Xpert at T0. Median follow-up was 23 (IQR 17-27) months. Sixty-eight (48.9%) patients failed AS, 65 (46.7%) are currently on AS, and 6 (4.3%) were lost at follow-up. At T0 57 (41.0%) patients had a negative test and 36 (63.2%) are still in AS. In patients with 2 consecutives negative Xpert tests, we could have avoided 73.9% of unnecessary cystoscopies, missing 26.4% failure, up to avoid all cystoscopies with 4 negative tests missing only 12% of failure. All the patients with negative Xpert had negative UC. Failure-free-survival at median follow-up (23 month) stratified for having 0, 1, or ≥2 negative tests was 67.0, 55.1. and 84.1, respectively.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that Xpert BC Monitor assay, when it is longitudinally repeated, could significantly reduce the number of unnecessary cystoscopies and UC during their follow-up.
Keywords: BIAS; NMIBC; Xpert BC; active surveillance; biomarker; cystoscopies; urine cytology.
Copyright © 2022 Fasulo, Paciotti, Lazzeri, Contieri, Casale, Saita, Lughezzani, Diana, Frego, Avolio, Colombo, Elefante, Guazzoni, Buffi, Bates and Hurle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical performance of Xpert Bladder Cancer (BC) Monitor, a mRNA-based urine test, in active surveillance (AS) patients with recurrent non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC): results from the Bladder Cancer Italian Active Surveillance (BIAS) project.World J Urol. 2020 Sep;38(9):2215-2220. doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-03002-3. Epub 2019 Nov 5. World J Urol. 2020. PMID: 31691083
-
Diagnostic value of Xpert® Bladder Cancer Monitor in the follow-up of patients affected by non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: an update.Ther Adv Urol. 2021 Mar 5;13:1756287221997183. doi: 10.1177/1756287221997183. eCollection 2021 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Urol. 2021. PMID: 33747133 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Xpert Bladder Cancer Monitor test performance for the detection of recurrence during non-muscle invasive bladder cancer follow-up.World J Urol. 2021 Sep;39(9):3329-3335. doi: 10.1007/s00345-021-03629-1. Epub 2021 Mar 26. World J Urol. 2021. PMID: 33770241 Free PMC article.
-
Xpert bladder cancer monitor in surveillance of bladder cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Urol Oncol. 2022 Apr;40(4):163.e1-163.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2021.08.017. Epub 2021 Sep 14. Urol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34535354
-
Urine-Based Biomarker Test Uromonitor® in the Detection and Disease Monitoring of Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Test Performance.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 11;16(4):753. doi: 10.3390/cancers16040753. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38398144 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Xpert Bladder Cancer Detection in Emergency Setting Assessment (XESA Project): A Prospective, Single-centre Trial.Eur Urol Open Sci. 2024 Dec 31;71:172-179. doi: 10.1016/j.euros.2024.09.001. eCollection 2025 Jan. Eur Urol Open Sci. 2024. PMID: 39845740 Free PMC article.
-
A Liquid Biopsy in Bladder Cancer-The Current Landscape in Urinary Biomarkers.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 2;23(15):8597. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158597. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distant metastasis without regional progression in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: case report and pooled analysis of literature.World J Surg Oncol. 2022 Jul 6;20(1):226. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02664-5. World J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35794571 Free PMC article.
-
The application value of multi-parameter cystoscope in improving the accuracy of preoperative bladder cancer grading.BMC Urol. 2022 Jul 18;22(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12894-022-01054-z. BMC Urol. 2022. PMID: 35850869 Free PMC article.
-
Active Surveillance in Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer, the Potential Role of Biomarkers: A Systematic Review.Curr Oncol. 2024 Apr 12;31(4):2201-2220. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31040163. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38668066 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

