Analysis of miRNAs Involved in Mouse Heart Injury Upon Coxsackievirus A2 Infection
- PMID: 35155276
- PMCID: PMC8831793
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.765445
Analysis of miRNAs Involved in Mouse Heart Injury Upon Coxsackievirus A2 Infection
Abstract
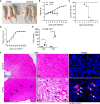
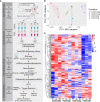
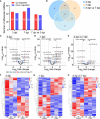
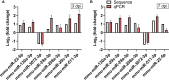
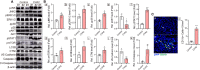
Coxsackievirus A2 (CVA2) has recently been constantly detected, and is associated with viral myocarditis in children. Our previous study demonstrated that CVA2 led to heart damage in a neonatal murine model. However, the molecular mechanism of heart injury caused by CVA2 remains largely unknown. Emerging evidence suggests the significant functions of miRNAs in Coxsackievirus infection. To investigate potential miRNAs involved in heart injury caused by CVA2, our study, for the first time, conducted a RNA-seq in vivo employing infected mice hearts. In total, 87, 101 and 76 differentially expressed miRNAs were identified at 3 days post infection (dpi), 7 dpi and 7 dpi vs 3 dpi. Importantly, above 3 comparison strategies shared 34 differentially expressed miRNAs. These results were confirmed by quantitative PCR (qPCR). Next, we did GO, KEGG, and miRNA-mRNA integrated analysis of differential miRNAs. The dual-luciferase reporter assay confirmed the miRNA-mRNA pairs. To further confirm the above enriched pathways and processes, we did Western blotting and immunofluorescence staining. Our results suggest that inflammatory responses, T cell activation, apoptosis, autophagy, antiviral immunity, NK cell infiltration, and the disruption of tight junctions are involved in the pathogenesis of heart injury caused by CVA2. The dysregulated miRNAs and pathways recognized in the current study can improve the understanding of the intricate interactions between CVA2 and the heart injury, opening a novel avenue for the future study of CVA2 pathogenesis.
Keywords: Coxsackievirus A2; RNA-seq; and mouth disease; foot; hand; miRNAs; molecular mechanism.
Copyright © 2022 Wu, Zhu, Qian, Hu, Ji, Li, Zhu, Liang and Jin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Ai Y., Zhang W., Wu J., Zhang J., Shen M., Yao S., et al. (2021). Molecular Epidemiology and Clinical Features of Enteroviruses-Associated Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease and Herpangina Outbreak in Zunyi, China, 2019. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 8, 656699. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.656699 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

