Factors Affecting the Fetal Fraction in Noninvasive Prenatal Screening: A Review
- PMID: 35155308
- PMCID: PMC8829468
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.812781
Factors Affecting the Fetal Fraction in Noninvasive Prenatal Screening: A Review
Abstract
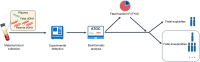
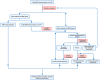
A paradigm shift in noninvasive prenatal screening has been made with the discovery of cell-free fetal DNA in maternal plasma. Noninvasive prenatal screening is primarily used to screen for fetal aneuploidies, and has been used globally. Fetal fraction, an important parameter in the analysis of noninvasive prenatal screening results, is the proportion of fetal cell-free DNA present in the total maternal plasma cell-free DNA. It combines biological factors and bioinformatics algorithms to interpret noninvasive prenatal screening results and is an integral part of quality control. Maternal and fetal factors may influence fetal fraction. To date, there is no broad consensus on the factors that affect fetal fraction. There are many different approaches to evaluate this parameter, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Different fetal fraction calculation methods may be used in different testing platforms or laboratories. This review includes numerous publications that focused on the understanding of the significance, influencing factors, and interpretation of fetal fraction to provide a deeper understanding of this parameter.
Keywords: cell-free fetal DNA; fetal fraction; genetic counseling; molecular genetics; noninvasive prenatal screening.
Copyright © 2022 Deng and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources