Targeting the microRNA-34a as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Cardiovascular Diseases
- PMID: 35155600
- PMCID: PMC8828972
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.784044
Targeting the microRNA-34a as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
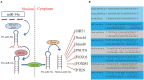
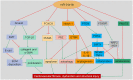
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are still the main cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide and include a group of disorders varying from vasculature, myocardium, arrhythmias and cardiac development. MicroRNAs (miRs) are endogenous non-coding RNAs with 18-23 nucleotides that regulate gene expression. The miR-34 family, including miR-34a/b/c, plays a vital role in the regulation of myocardial physiology and pathophysiological processes. Recently, miR-34a has been implicated in cardiovascular fibrosis, dysfunction and related cardiovascular disorders as an essential regulator. Interestingly, there is a pivotal link among miR-34a, cardiovascular fibrosis, and Smad4/TGF-β1 signaling. Notably, both loss-of-function and gain-of-function approaches identified the critical roles of miR-34a in cardiovascular apoptosis, autophagy, inflammation, senescence and remodeling by modulating multifunctional signaling pathways. In this article, we focus on the current understanding of miR-34a in biogenesis, its biological effects and its implications for cardiac pathologies including myocardial infarction, heart failure, ischaemia reperfusion injury, cardiomyopathy, atherosclerosis, hypertension and atrial fibrillation. Thus, further understanding of the effects of miR-34a on cardiovascular diseases will aid the development of effective interventions. Targeting for miR-34a has emerged as a potential therapeutic target for cardiovascular dysfunction and related diseases.
Keywords: apoptosis; cardiovascular fibrosis; heart dysfunction; microRNA-34a; myocardial remodeling.
Copyright © 2022 Hua, Liu, Liang, Wang and Zhong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

