Thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms during cytoreductive and antithrombotic drug treatment
- PMID: 35155976
- PMCID: PMC8822262
- DOI: 10.1002/rth2.12657
Thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms during cytoreductive and antithrombotic drug treatment
Abstract
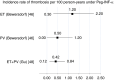
A state-of-the-art lecture titled "Myeloproliferative Neoplasm-associated Thrombosis" was presented at the ISTH congress in 2021. We summarize here the main points of the lecture with two purposes: to report the incidence rates of major thrombosis in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia and to discuss to what extent cytoreductive therapy and antithrombotic drugs have reduced the incidence of these events. Unfortunately, the incidence rate of thrombosis remains high, ranging between 2 and 5/100 person-years. It is likely that new drugs such as interferon and ruxolitinib can be more efficacious given their cytoreductive and anti-inflammatory activities. Despite prophylaxis with vitamin K antagonists and direct oral anticoagulants after venous thrombosis in either common sites or splanchnic or cerebral sites, the incidence rate is still elevated, as high as 4 to 5/100 person-years. Future studies with new drugs or new strategies should consider thrombosis as the primary endpoint or surrogate biomarkers only if previously validated.
Keywords: antithrombotic drugs; cytoreduction; epidemiology; myeloproliferative neoplasm; thrombosis.
© 2022 The Authors. Research and Practice in Thrombosis and Haemostasis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH).
Figures

References
-
- Tefferi A, Pardanani A. Essential thrombocythemia. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:2135‐2144. - PubMed
-
- Hasselbalch HC, Elvers M, Schafer AI. The pathobiology of thrombosis, microvascular disease, and hemorrhage in the myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood. 2021;137:2152‐2160. - PubMed
-
- Barbui T, Finazzi G, Falanga A. Myeloproliferative neoplasms and thrombosis. Blood. 2013;122:2176‐2184. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

