Surgical Soft Tissue Management for Glenohumeral Deformity and Contractures in Brachial Plexus Birth Injury : A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 35156170
- PMCID: PMC9076768
- DOI: 10.1007/s12178-022-09747-6
Surgical Soft Tissue Management for Glenohumeral Deformity and Contractures in Brachial Plexus Birth Injury : A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose of the review: Consensus on the effects of soft tissue surgical intervention in the management of brachial plexus birth injury (BPBI) sequalae is lacking. The purpose of this review is to examine the available literature on the functional and structural outcomes following soft tissue surgical management of BPBI sequalae.
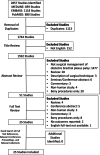
Recent findings: EMBASE, PubMed, and MEDLINE were searched for related literature from the point of database inception until April 2021. Relevant papers were screened by two reviewers independently and in duplicate. A meta-analysis was performed using a random effects model. A total of 25 studies (852 patients) were included in the review, with the number included in each meta-analysis varying based on outcome of interest. There were significant improvements from pre- to post-operative time points for the following measures: Mallet aggregate scores (5.0 points, p<0.0001), active external rotation in adduction (48.9°, p=0.003), passive external rotation in adduction (64.6°, p< 0.00001), active abduction (46.2°, p<0.00001), glenoid version (14.4°, p< 0.00001), and percentage of the humeral head anterior to the scapular line (17.53°, p< 0.00001). Furthermore, data revealed an overall complication rate of 9.3% (79/852 patients) and a major complication rate of 0.47% (4/852 patients). Patients with BPBI sequela experience statistically significant improvements in functional, structural, and range of motion outcomes of the GH joint following soft tissue surgical management. Understanding the ideal indications for each procedure and age of surgical management with future prospective studies will help to optimize surgical management of these patients.
Keywords: Brachial plexus neuropathies; Orthopaedics; Shoulder joint.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose. The authors declare they have no funding to disclose.
Figures

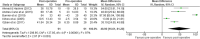



Similar articles
-
Shoulder internal rotation contracture in brachial plexus birth injury: proximal or distal subscapularis release?J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2021 May;30(5):1117-1127. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2020.08.001. Epub 2020 Aug 25. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2021. PMID: 32853791
-
The early effects of tendon transfers and open capsulorrhaphy on glenohumeral deformity in brachial plexus birth palsy.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008 Oct;90(10):2171-9. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.G.01517. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008. PMID: 18829915
-
Glenohumeral abduction contracture in children with unresolved neonatal brachial plexus palsy.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015 Jan 21;97(2):112-8. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.N.00203. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015. PMID: 25609437
-
External rotation humeral osteotomy for brachial plexus birth palsy.Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2007 Mar;11(1):8-14. doi: 10.1097/01.bth.0000248359.14448.e6. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2007. PMID: 17536517 Review.
-
Glenohumeral deformity in children with brachial plexus birth injuries.Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2011;69(1):36-43. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2011. PMID: 21332437 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative Musculoskeletal Imaging of the Pediatric Shoulder.Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2024 Oct 1;103(10):955-964. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000002515. Epub 2024 Apr 6. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38713590 Review.
-
Surgical Treatment of Obstetric Plexus Lesions by Direct Coaptation Compared to Sural Nerve Graft Interposition.J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj. 2025 Jan 15;20(1):e9-e15. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1801398. eCollection 2025 Jan. J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj. 2025. PMID: 39816324 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

