Evaluation of Monoexponential, Stretched-Exponential and Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MRI Diffusion Models in Early Response Monitoring to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients With Breast Cancer-A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 35156741
- PMCID: PMC9543625
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.28113
Evaluation of Monoexponential, Stretched-Exponential and Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MRI Diffusion Models in Early Response Monitoring to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients With Breast Cancer-A Preliminary Study
Abstract
Background: There has been a growing interest in exploring the applications of stretched-exponential (SEM) and intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) models of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in breast imaging, with the focus on differentiation of breast lesions. However, the use of SEM and IVIM models to predict early response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) has received less attention.
Purpose: To investigate the value of monoexponential, SEM, and IVIM models to predict early response to NACT in patients with primary breast cancer.
Study type: Prospective.
Population: Thirty-seven patients with primary breast cancer (aged 46 ± 11 years) due to undergo NACT.
Field strength/sequences: A 1.5-T MR scanner, T1 -weighted three-dimensional spoiled gradient-echo, two-dimensional single-shot spin-echo echo-planar imaging sequence (DWI) at six b-values (0-800 s mm-2 ).
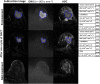
Assessment: Tumor volume, apparent diffusion coefficient, tissue diffusion (Dt ), pseudo-diffusion coefficient (Dp ), perfusion fraction (f), distributed diffusion coefficient, and alpha (α) were extracted, following volumetric sampling of the tumors, at three time-points: pretreatment, post one and three cycles of NACT.
Statistical tests: Mann-Whitney test, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Statistical significance level was P < 0.05.
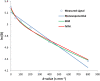
Results: Following NACT, 17 patients were determined to be pathological responders and 20 nonresponders. Tumor volume was significantly larger in nonresponders at each MRI time-point and demonstrated reasonable performance in predicting response (area under the ROC curve [AUC] = 0.83-0.87). No significant differences between groups were found in the diffusion coefficients at each time-point (P = 0.09-1). The parameters α (SEM), f, and f × Dp (IVIM) were able to differentiate between response groups after one cycle of NACT (AUC = 0.73, 0.72, and 0.74, respectively).
Conclusion: Diffusion coefficients derived from the monoexponential, SEM, and IVIM models did not predict pathological response. However, the IVIM-derived parameters f and f × Dp and the SEM-derived parameter α were able to predict response to NACT in breast cancer patients following one cycle of NACT.
Level of evidence: 2 TECHNICAL EFFICACY STAGE: 2.
Keywords: breast cancer; diffusion-weighted MRI; imaging biomarkers; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; quantitative evaluation.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures

Comment in
-
Editorial for "Evaluation of Monoexponential, Stretched Exponential and Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MRI Diffusion Models in Early Response Monitoring to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients With Breast Cancer-A Preliminary Study".J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022 Oct;56(4):1089-1090. doi: 10.1002/jmri.28118. Epub 2022 Feb 18. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35179266 No abstract available.
References
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group . Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15‐year survival: An overview of the randomised trials. Lancet 2005;365(9472):1687‐1717. - PubMed
-
- Kaufmann M, Von Minckwitz G, Mamounas EP, et al. Recommendations from an international consensus conference on the current status and future of neoadjuvant systemic therapy in primary breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2012;19(5):1508‐1516. - PubMed
-
- Shenoy H, Peter M, Masannat Y, Dall B, Dodwell D, Horgan KJSO. Practical advice on clinical decision making during neoadjuvant chemotherapy for primary breast cancer. Surg Oncol 2009;1(18):65‐71. - PubMed
-
- Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 2009;45(2):228‐247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

