Inhibition of phosphodiesterase-4 in the spinal dorsal horn ameliorates neuropathic pain via cAMP-cytokine-Cx43 signaling in mice
- PMID: 35156776
- PMCID: PMC8981432
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.13807
Inhibition of phosphodiesterase-4 in the spinal dorsal horn ameliorates neuropathic pain via cAMP-cytokine-Cx43 signaling in mice
Abstract
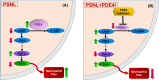
Background: The spinal phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) plays an important role in chronic pain. Inhibition of PDE4, an enzyme catalyzing the hydrolysis of cyclic adenosine monophosphate AMP (cAMP), produces potent antinociceptive activity. However, the antinociceptive mechanism remains largely unknown. Connexin43 (Cx43), a gap junction protein, has been shown to be involved in controlling pain transduction at the spinal level; restoration of Cx43 expression in spinal astrocytes to the normal levels reduces nerve injury-induced pain. Here, we evaluate the novel mechanisms involving spinal cAMP-Cx43 signaling by which PDE4 inhibitors produce antinociceptive activity.
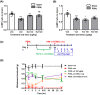
Methods: First, we determined the effect of PDE4 inhibitors rolipram and roflumilast on partial sciatic nerve ligation (PSNL)-induced mechanical hypersensitivity. Next, we observed the role of cAMP-Cx43 signaling in the effect of PDE4 inhibitors on PSNL-induced mechanical hypersensitivity.
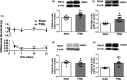
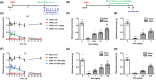
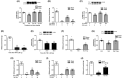
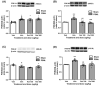
Results: Single or repeated, intraperitoneal or intrathecal administration of rolipram or roflumilast significantly reduced mechanical hypersensitivity in mice following PSNL. In addition, repeated intrathecal treatment with either of PDE4 inhibitors reduced PSNL-induced downregulation of cAMP and Cx43, and upregulation of proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β. Furthermore, the antinociceptive effects of PDE4 inhibitors were attenuated by the protein kinase A (PKA) inhibitor H89, TNF-α, or Cx43 antagonist carbenoxolone. Finally, PSNL-induced upregulation of PDE4B and PDE4D, especially the PDE4B subtype, was reduced by treatment with either of the PDE4 inhibitors.
Conclusions: The results suggest that the antinociceptive effect of PDE4 inhibitors is contributed by increasing Cx43 expression via cAMP-PKA-cytokine signaling in the spinal dorsal horn.
Keywords: connexin43; neuropathic pain; phosphodiesterase-4; roflumilast; rolipram.
© 2022 The Authors. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
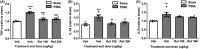
Similar articles
-
Tumor necrosis factor-mediated downregulation of spinal astrocytic connexin43 leads to increased glutamatergic neurotransmission and neuropathic pain in mice.Brain Behav Immun. 2015 Oct;49:293-310. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.06.015. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Brain Behav Immun. 2015. PMID: 26116449
-
Lycopene ameliorates neuropathic pain by upregulating spinal astrocytic connexin 43 expression.Life Sci. 2016 Jun 15;155:116-22. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.05.021. Epub 2016 May 16. Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27197028
-
Downregulation of spinal astrocytic connexin43 leads to upregulation of interleukin-6 and cyclooxygenase-2 and mechanical hypersensitivity in mice.Glia. 2018 Feb;66(2):428-444. doi: 10.1002/glia.23255. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Glia. 2018. PMID: 29105869
-
Molecular Properties of Phosphodiesterase 4 and Its Inhibition by Roflumilast and Cilomilast.Molecules. 2025 Feb 4;30(3):692. doi: 10.3390/molecules30030692. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39942796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) and neurological disorders: A promising frontier in neuropharmacology.Adv Pharmacol. 2025;102:159-209. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2024.10.005. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Adv Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39929579 Review.
Cited by
-
Connexins and Pannexins: Important Players in Neurodevelopment, Neurological Diseases, and Potential Therapeutics.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 9;10(9):2237. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092237. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36140338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropathic pain, antidepressant drugs, and inflammation: a narrative review.J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2024 Sep 27;4(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s44158-024-00204-z. J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2024. PMID: 39334307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide association study on chronic postsurgical pain after abdominal surgeries in the UK Biobank.Anaesthesia. 2025 May;80(5):499-510. doi: 10.1111/anae.16528. Epub 2024 Dec 29. Anaesthesia. 2025. PMID: 39734325 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokines reprogram airway sensory neurons in asthma.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 18:2023.01.26.525731. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.26.525731. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell Rep. 2024 Dec 24;43(12):115045. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.115045. PMID: 39345572 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The Double-Edged Effect of Connexins and Pannexins of Glial Cells in Central and Peripheral Nervous System After Nerve Injury.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 May 1. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04991-6. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40310549 Review.
References
-
- Kobayashi Y, Kiguchi N, Maeda T, Ozaki M, Kishioka S. The critical role of spinal ceramide in the development of partial sciatic nerve ligation‐induced neuropathic pain in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;421:318‐322. - PubMed
-
- Même W, Calvo CF, Froger N, et al. Proinflammatory cytokines released from microglia inhibit gap junctions in astrocytes: potentiation by beta‐amyloid. FASEB J. 2006;20:494‐496. - PubMed
-
- Zhang FF, Morioka N, Nakashima‐Hisaoka K, Nakata Y. Spinal astrocytes stimulated by tumor necrosis factor‐ α and/or interferon‐γ attenuate connexin 43‐gap junction via c‐jun terminal kinase activity. J Neurosci Res. 2013;91:745‐756. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

