Three-dimensional multi-site random access photostimulation (3D-MAP)
- PMID: 35156923
- PMCID: PMC8843094
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.73266
Three-dimensional multi-site random access photostimulation (3D-MAP)
Abstract
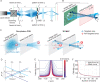
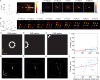
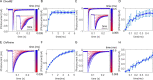
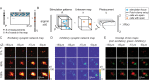
Optical control of neural ensemble activity is crucial for understanding brain function and disease, yet no technology can achieve optogenetic control of very large numbers of neurons at an extremely fast rate over a large volume. State-of-the-art multiphoton holographic optogenetics requires high-power illumination that only addresses relatively small populations of neurons in parallel. Conversely, one-photon holographic techniques can stimulate more neurons with two to three orders lower power, but with limited resolution or addressable volume. Perhaps most problematically, two-photon holographic optogenetic systems are extremely expensive and sophisticated which has precluded their broader adoption in the neuroscience community. To address this technical gap, we introduce a new one-photon light sculpting technique, three-dimensional multi-site random access photostimulation (3D-MAP), that overcomes these limitations by modulating light dynamically, both in the spatial and in the angular domain at multi-kHz rates. We use 3D-MAP to interrogate neural circuits in 3D and demonstrate simultaneous photostimulation and imaging of dozens of user-selected neurons in the intact mouse brain in vivo with high spatio-temporal resolution. 3D-MAP can be broadly adopted for high-throughput all-optical interrogation of brain circuits owing to its powerful combination of scale, speed, simplicity, and cost.
Keywords: brain mapping; calcium imaging; light field; mouse; neural circuit; neuroscience; optical microscopy; optogenetics; structured illumination; visual cortex.
© 2022, Xue et al.
Conflict of interest statement
YX, LW, HA, NP No competing interests declared
Figures









Similar articles
-
Holographic microscope and its biological application.Neurosci Res. 2022 Jun;179:57-64. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2021.10.012. Epub 2021 Nov 2. Neurosci Res. 2022. PMID: 34740727 Review.
-
Temperature Rise under Two-Photon Optogenetic Brain Stimulation.Cell Rep. 2018 Jul 31;24(5):1243-1253.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.06.119. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30067979
-
Holographic imaging and photostimulation of neural activity.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018 Jun;50:211-221. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2018.03.006. Epub 2018 Apr 13. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29660600 Review.
-
Temporally precise single-cell-resolution optogenetics.Nat Neurosci. 2017 Dec;20(12):1796-1806. doi: 10.1038/s41593-017-0018-8. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Nat Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29184208 Free PMC article.
-
Submillisecond Optogenetic Control of Neuronal Firing with Two-Photon Holographic Photoactivation of Chronos.J Neurosci. 2017 Nov 1;37(44):10679-10689. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1246-17.2017. Epub 2017 Oct 2. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28972125 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Computational optics for high-throughput imaging of neural activity.Neurophotonics. 2022 Oct;9(4):041408. doi: 10.1117/1.NPh.9.4.041408. Epub 2022 May 20. Neurophotonics. 2022. PMID: 35607516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiphoton Neurophotonics: Recent Advances in Imaging and Manipulating Neuronal Circuits.ACS Photonics. 2025 Apr 4;12(7):3296-3318. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.4c02101. eCollection 2025 Jul 16. ACS Photonics. 2025. PMID: 40693197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in computer-generated holography for targeted neuronal modulation.Neurophotonics. 2022 Oct;9(4):041409. doi: 10.1117/1.NPh.9.4.041409. Epub 2022 Jun 16. Neurophotonics. 2022. PMID: 35719844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Three-dimensional random-access confocal microscopy with 3D remote focusing system.Commun Eng. 2024 Nov 11;3(1):166. doi: 10.1038/s44172-024-00320-2. Commun Eng. 2024. PMID: 39528669 Free PMC article.
-
Probing neural codes with two-photon holographic optogenetics.Nat Neurosci. 2021 Oct;24(10):1356-1366. doi: 10.1038/s41593-021-00902-9. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Nat Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34400843 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adam Y, Kim JJ, Lou S, Zhao Y, Xie ME, Brinks D, Wu H, Mostajo-Radji MA, Kheifets S, Parot V, Chettih S, Williams KJ, Gmeiner B, Farhi SL, Madisen L, Buchanan EK, Kinsella I, Zhou D, Paninski L, Harvey CD, Zeng H, Arlotta P, Campbell RE, Cohen AE. Voltage imaging and optogenetics reveal behaviour-dependent changes in hippocampal dynamics. Nature. 2019;569:413–417. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1166-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Botcherby EJ, Juškaitis R, Booth MJ, Wilson T. An optical technique for remote focusing in microscopy. Optics Communications. 2008;281:880–887. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2007.10.007. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

