Estimated Cost-effectiveness of Medical Therapy, Sleeve Gastrectomy, and Gastric Bypass in Patients With Severe Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 35157054
- PMCID: PMC8845022
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.48317
Estimated Cost-effectiveness of Medical Therapy, Sleeve Gastrectomy, and Gastric Bypass in Patients With Severe Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
Importance: Bariatric surgery is recommended for patients with severe obesity (body mass index ≥40) and type 2 diabetes (T2D). However, the most cost-effective treatment remains unclear and may depend on the patient's T2D severity.
Objective: To estimate the cost-effectiveness of medical therapy, sleeve gastrectomy (SG), and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) among patients with severe obesity and T2D, stratified by T2D severity.
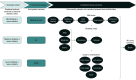
Design, setting, and participants: This economic evaluation used a microsimulation model to project health and cost outcomes of medical therapy, SG, and RYGB over 5 years. Time horizons varied between 10 and 30 years in sensitivity analyses. Model inputs were derived from clinical trials, large cohort studies, national databases, and published literature. Probabilistic sampling of model inputs accounted for parameter uncertainty. Estimates of US adults with severe obesity and T2D were derived from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Data analysis was performed from January 2020 to August 2021.
Exposures: Medical therapy, SG, and RYGB.
Main outcomes and measures: Quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs), costs (in 2020 US dollars), and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) were projected, with future cost and QALYs discounted 3.0% annually. A strategy was deemed cost-effective if the ICER was less than $100 000 per QALY. The preferred strategy resulted in the greatest number of QALYs gained while being cost-effective.
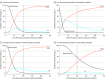
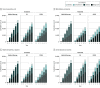
Results: The model simulated 1000 cohorts of 10 000 patients, of whom 16% had mild T2D, 56% had moderate T2D, and 28% had severe T2D at baseline. The mean age of simulated patients was 54.6 years (95% CI, 54.2-55.0 years), 61.6% (95% CI, 60.1%-63.4%) were female, and 65.1% (95% CI, 63.6%-66.7%) were non-Hispanic White. Compared with medical therapy over 5 years, RYGB was associated with the most QALYs gained in the overall population (mean, 0.44 QALY; 95% CI, 0.21-0.86 QALY) and when stratified by baseline T2D severity: mild (mean, 0.59 QALY; 95% CI, 0.35-0.98 QALY), moderate (mean, 0.50 QALY; 95% CI, 0.25-0.88 QALY), and severe (mean, 0.30 QALY; 95% CI, 0.07-0.79 QALY). RYGB was the preferred strategy in the overall population (ICER, $46 877 per QALY; 83.0% probability preferred) and when stratified by baseline T2D severity: mild (ICER, $36 479 per QALY; 73.7% probability preferred), moderate (ICER, $37 056 per QALY; 85.6% probability preferred), and severe (ICER, $98 940 per QALY; 40.2% probability preferred). The cost-effectiveness of RYGB improved over a longer time horizon.
Conclusions and relevance: These findings suggest that the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of bariatric surgery vary by baseline severity of T2D. Over a 5-year time horizon, RYGB is projected to be the preferred treatment strategy for patients with severe obesity regardless of baseline T2D severity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bariatric surgery for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus requiring insulin: Clinical outcome and cost-effectiveness analyses.PLoS Med. 2020 Dec 7;17(12):e1003228. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003228. eCollection 2020 Dec. PLoS Med. 2020. PMID: 33285553 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-Utility of Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass in Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity with a BMI ≥ 27.5 kg/m2: a Multi-Center Study with a 4-Year Follow-Up of Surgical Cohort.Obes Surg. 2019 Dec;29(12):3978-3986. doi: 10.1007/s11695-019-04069-y. Obes Surg. 2019. PMID: 31338737 Clinical Trial.
-
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Bariatric Surgery for Morbid Obesity.Obes Surg. 2018 Aug;28(8):2203-2214. doi: 10.1007/s11695-017-3100-0. Obes Surg. 2018. PMID: 29335933
-
The cost-effectiveness of bariatric surgery.Am J Gastroenterol. 2003 Sep;98(9):2097-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07671.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 14499794 Review.
-
Bariatric procedure selection in patients with type 2 diabetes: choice between Roux-en-Y gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy.Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2020 Feb;16(2):332-339. doi: 10.1016/j.soard.2019.11.013. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2020. PMID: 31902579 Review.
Cited by
-
Power-assisted Liposuction for Lymphedema: A Cost-utility Analysis.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2022 Nov 18;10(11):e4671. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000004671. eCollection 2022 Nov. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2022. PMID: 36415620 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized Controlled Trial Based US Commercial Payor Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty Versus Lifestyle Modification Alone for Adults With Class I/II Obesity.Obes Surg. 2024 Sep;34(9):3275-3284. doi: 10.1007/s11695-024-07324-z. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Obes Surg. 2024. PMID: 39107454 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of Bariatric Surgery in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Case Report and Literature Review.Cureus. 2023 Oct 27;15(10):e47843. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47843. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38021602 Free PMC article.
-
International expert consensus on surgery for type 2 diabetes mellitus.BMC Endocr Disord. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s12902-025-01961-w. BMC Endocr Disord. 2025. PMID: 40598146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medication cost for treatment of metabolic dysregulation decreases following adolescent bariatric surgery.Surg Endosc. 2025 Aug;39(8):5214-5219. doi: 10.1007/s00464-025-11920-0. Epub 2025 Jun 26. Surg Endosc. 2025. PMID: 40571792
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . National diabetes statistics report, 2020: estimates of diabetes and its burden in the United States. September 28, 2020. Accessed April 8, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html
-
- McTigue KM, Wellman R, Nauman E, et al. ; PCORnet Bariatric Study Collaborative . Comparing the 5-year diabetes outcomes of sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass: the national Patient-Centered Clinical Research Network (PCORNet) bariatric study. JAMA Surg. 2020;155(5):e200087-e200087. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2020.0087 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

