SARS-CoV-2 interacts with renin-angiotensin system: impact on the central nervous system in elderly patients
- PMID: 35157210
- PMCID: PMC8853071
- DOI: 10.1007/s11357-022-00528-0
SARS-CoV-2 interacts with renin-angiotensin system: impact on the central nervous system in elderly patients
Abstract
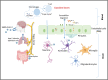
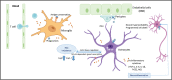
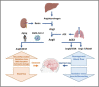
SARS-CoV-2 is a recently identified coronavirus that causes the current pandemic disease known as COVID-19. SARS-CoV-2 uses angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a receptor, suggesting that the initial steps of SARS-CoV-2 infection may have an impact on the renin-angiotensin system (RAS). Several processes are influenced by RAS in the brain. The neurological symptoms observed in COVID-19 patients, including reduced olfaction, meningitis, ischemic stroke, cerebral thrombosis, and delirium, could be associated with RAS imbalance. In this review, we focus on the potential role of disturbances in the RAS as a cause for central nervous system sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection in elderly patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; Central nervous system; Elderly; Renin-angiotensin system; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to American Aging Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brain Renin-Angiotensin System: From Physiology to Pathology in Neuronal Complications Induced by SARS-CoV-2.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2023 Aug 4;2023:8883492. doi: 10.1155/2023/8883492. eCollection 2023. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2023. PMID: 37575318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 Receptor and Regulator of the Renin-Angiotensin System: Celebrating the 20th Anniversary of the Discovery of ACE2.Circ Res. 2020 May 8;126(10):1456-1474. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317015. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Circ Res. 2020. PMID: 32264791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A mechanistic model and therapeutic interventions for COVID-19 involving a RAS-mediated bradykinin storm.Elife. 2020 Jul 7;9:e59177. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59177. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32633718 Free PMC article.
-
Covid-19: the renin-angiotensin system imbalance hypothesis.Clin Sci (Lond). 2020 Jun 12;134(11):1259-1264. doi: 10.1042/CS20200492. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32507883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: A Potential Target to Prevent COVID-19?Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Oct 22;12:725967. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.725967. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34745001 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of ACE2 in Neurological Disorders: From Underlying Mechanisms to the Neurological Impact of COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 15;25(18):9960. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189960. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of Vitamin D Signaling Impairs Adaptation of Cerebrocortical Microcirculation to Carotid Artery Occlusion in Hyperandrogenic Female Mice.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 5;15(18):3869. doi: 10.3390/nu15183869. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37764653 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Exacerbates Neurovascular Uncoupling and Contributes to Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 18;14(12):1621. doi: 10.3390/biom14121621. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766328 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship among SARS-CoV-2, Vaccine Spike Protein, Renin- Angiotensin System, and Epilepsy.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2025;25(3):e18715265350339. doi: 10.2174/0118715265350339240919053408. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2025. PMID: 39313888 No abstract available.
-
The route of SARS-CoV-2 to brain infection: have we been barking up the wrong tree?Mol Neurodegener. 2022 Mar 15;17(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s13024-022-00529-9. Mol Neurodegener. 2022. PMID: 35292068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walker PJ, Siddell SG, Lefkowitz EJ, Mushegian AR, Dempsey DM, Dutilh BE, Harrach B, Harrison RL, Hendrickson RC, Junglen S, Knowles NJ, Kropinski AM, Krupovic M, Kuhn JH, Nibert M, Rubino L, Sabanadzovic S, Simmonds P, Varsani A, Zerbini FM, Davison AJ. Changes to virus taxonomy and the International Code of Virus Classification and Nomenclature ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2019) Arch Virol. 2019;164:2417–2429. doi: 10.1007/s00705-019-04306-w. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wiersinga WJ. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in the Netherlands. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2020;164:D5021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

