SARS-CoV-2 infection causes intestinal cell damage: Role of interferon's imbalance
- PMID: 35158258
- PMCID: PMC8828414
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2022.155826
SARS-CoV-2 infection causes intestinal cell damage: Role of interferon's imbalance
Abstract
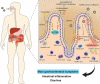
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the causative agent of the newly emerging lung disease pandemic COVID-19. This viral infection causes a series of respiratory disorders, and although this virus mainly infects respiratory cells, the small intestine can also be an important site of entry or interaction, as enterocytes highly express in angiotensin-2 converting enzyme (ACE) receptors. There are countless reports pointing to the importance of interferons (IFNs) with regard to the mediation of the immune system in viral infection by SARS-CoV-2. Thus, this review will focus on the main cells that make up the large intestine, their specific immunology, as well as the function of IFNs in the intestinal mucosa after the invasion of coronavirus-2.
Keywords: Cytokines; Interferons; SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Grajales-Reyes G.E., Colonna M. Interferon responses in viral pneumonias. Science. 2020;369:626–627. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO), Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic: Numbers at a glance (2020). https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed 15 October 2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

