Early Predictor Tool of Disease Using Label-Free Liquid Biopsy-Based Platforms for Patient-Centric Healthcare
- PMID: 35159085
- PMCID: PMC8834418
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14030818
Early Predictor Tool of Disease Using Label-Free Liquid Biopsy-Based Platforms for Patient-Centric Healthcare
Abstract
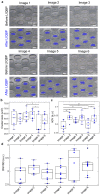
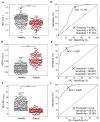
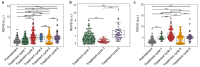
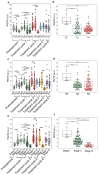
Cancer cells undergo phenotypic changes or mutations during treatment, making detecting protein-based or gene-based biomarkers challenging. Here, we used algorithmic analysis combined with patient-derived tumor models to derive an early prediction tool using patient-derived cell clusters from liquid biopsy (LIQBP) for cancer prognosis in a label-free manner. The LIQBP platform incorporated a customized microfluidic biochip that mimicked the tumor microenvironment to establish patient clusters, and extracted physical parameters from images of each sample, including size, thickness, roughness, and thickness per area (n = 31). Samples from healthy volunteers (n = 5) and cancer patients (pretreatment; n = 4) could be easily distinguished with high sensitivity (91.16 ± 1.56%) and specificity (71.01 ± 9.95%). Furthermore, we demonstrated that the multiple unique quantitative parameters reflected patient responses. Among these, the ratio of normalized gray value to cluster size (RGVS) was the most significant parameter correlated with cancer stage and treatment duration. Overall, our work presented a novel and less invasive approach for the label-free prediction of disease prognosis to identify patients who require adjustments to their treatment regime. We envisioned that such efforts would promote the management of personalized patient care conveniently and cost effectively.
Keywords: algorithmic analysis; disease prognosis; label free; patient-derived cell clusters; personalized patient care.
Conflict of interest statement
One or more authors have a patent related to this work.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

