ATP8B1 Knockdown Activated the Choline Metabolism Pathway and Induced High-Level Intracellular REDOX Homeostasis in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 35159102
- PMCID: PMC8834475
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14030835
ATP8B1 Knockdown Activated the Choline Metabolism Pathway and Induced High-Level Intracellular REDOX Homeostasis in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
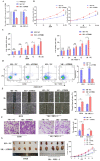
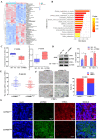
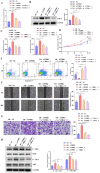
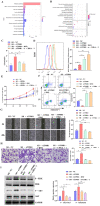
The flippase ATPase class I type 8b member 1 (ATP8B1) is essential for maintaining the stability and polarity of the epithelial membrane and can translocate specific phospholipids from the outer membrane to the inner membrane of the cell. Although ATP8B1 plays important roles in cell functions, ATP8B1 has been poorly studied in tumors and its prognostic value in patients with lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) remains unclear. By investigating the whole genomic expression profiles of LUSC samples from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database and Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital (TJMUCH) cohort, we found that low expression of ATP8B1 was associated with poor prognosis of LUSC patients. The results from cellular experiments and a xenograft-bearing mice model indicated that ATP8B1 knockdown firstly induced mitochondrial dysfunction and promoted ROS production. Secondly, ATP8B1 knockdown promoted glutathione synthesis via upregulation of the CHKA-dependent choline metabolism pathway, therefore producing and maintaining high-level intracellular REDOX homeostasis to aggravate carcinogenesis and progression of LUSC. In summary, we proposed ATP8B1 as a novel predictive biomarker in LUSC and targeting ATP8B1-driven specific metabolic disorder might be a promising therapeutic strategy for LUSC.
Keywords: ATP8B1; CHKA; LUSC; REDOX.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of ATP8B1 as a Tumor Suppressor Gene for Colorectal Cancer and Its Involvement in Phospholipid Homeostasis.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Sep 29;2020:2015648. doi: 10.1155/2020/2015648. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33062669 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of an individualized prognostic signature of lung squamous cell carcinoma based on ferroptosis-related genes.Thorac Cancer. 2021 Dec;12(23):3236-3247. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14195. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34672420 Free PMC article.
-
The phospholipid flippase ATP8B1 is required for lysosomal fusion in macrophages.Cell Biochem Funct. 2022 Dec;40(8):914-925. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3752. Epub 2022 Sep 28. Cell Biochem Funct. 2022. PMID: 36169099 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical value of miR-182-5p in lung squamous cell carcinoma: a study combining data from TCGA, GEO, and RT-qPCR validation.World J Surg Oncol. 2018 Apr 10;16(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12957-018-1378-6. World J Surg Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29636077 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and Validation of Prognostic Regulation Network Based on RNA-Binding Protein Genes in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma.DNA Cell Biol. 2021 Dec;40(12):1563-1583. doi: 10.1089/dna.2021.0145. DNA Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34931870
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-375 restrains the progression of lung squamous cell carcinoma by modulating the ERK pathway via UBE3A-mediated DUSP1 degradation.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Jun 29;9(1):199. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01499-7. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 37385985 Free PMC article.
-
Type IV P-Type ATPases: Recent Updates in Cancer Development, Progression, and Treatment.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 30;15(17):4327. doi: 10.3390/cancers15174327. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37686603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Sex and Obesity on the Gene Expression of Lipid Flippases in Adipose Tissue.J Clin Med. 2022 Jul 4;11(13):3878. doi: 10.3390/jcm11133878. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35807162 Free PMC article.
-
A novel interplay between bacteria and metabolites in different early-stage lung cancer: an integrated microbiome and metabolome analysis.Front Oncol. 2025 Jan 7;14:1492571. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1492571. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39839794 Free PMC article.
-
Flipping the script: Advances in understanding how and why P4-ATPases flip lipid across membranes.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2024 Apr;1871(4):119700. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2024.119700. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 38382846 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

