Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based COVID-19 Therapy: Bioengineering Perspectives
- PMID: 35159275
- PMCID: PMC8834073
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11030465
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based COVID-19 Therapy: Bioengineering Perspectives
Abstract
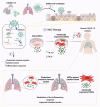
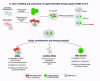
The novel pathogenic severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are currently utilized in clinics for pulmonary inflammatory diseases, including acute respiratory distress syndrome and acute lung injury. Given that MSCs offer a promising treatment against COVID-19, they are being used against COVID-19 in more than 70 clinical trials with promising findings. Genetically engineered MSCs offer promising therapeutic options in pulmonary diseases. However, their potential has not been explored yet. In this review, we provide perspectives on the functionally modified MSCs that can be developed and harnessed for COVID-19 therapy. Options to manage the SARS-CoV-2 infection and its variants using various bioengineering tools to increase the therapeutic efficacy of MSCs are highlighted.
Keywords: ACE2; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; TMPRSS2; bioengineering; genetic engineering; mesenchymal stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heterogeneous expression of ACE2 and TMPRRS2 in mesenchymal stromal cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Jan;26(1):228-234. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17048. Epub 2021 Nov 24. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34821008 Free PMC article.
-
Potential roles of mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes in the treatment of COVID-19.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2021 Oct 30;26(10):948-961. doi: 10.52586/4999. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2021. PMID: 34719217 Review.
-
A safety consideration of mesenchymal stem cell therapy on COVID-19.Stem Cell Res. 2020 Dec;49:102066. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2020.102066. Epub 2020 Oct 24. Stem Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 33242791 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-based treatments for COVID-19: status and future perspectives for clinical applications.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Feb 20;79(3):142. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04096-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35187617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiological Relevance of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 As a Metabolic Linker and Therapeutic Implication of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in COVID-19 and Hypertension.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021 Feb;17(1):132-143. doi: 10.1007/s12015-020-10012-x. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021. PMID: 32748331 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunomodulatory effect of IFN-γ licensed adipose-mesenchymal stromal cells in an in vitro model of inflammation generated by SARS-CoV-2 antigens.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 16;14(1):24235. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75776-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39415027 Free PMC article.
-
Precise nanoscale fabrication technologies, the "last mile" of medicinal development.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025 May;15(5):2372-2401. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2025.03.040. Epub 2025 Mar 18. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025. PMID: 40487646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanotransduction in Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) Differentiation: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 21;23(9):4580. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094580. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35562971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Clinical Update on SARS-CoV-2: Pathology and Development of Potential Inhibitors.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Jan 4;45(1):400-433. doi: 10.3390/cimb45010028. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36661514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Immunomodulatory Role of Cell-Free Approaches in SARS-CoV-2-Induced Cytokine Storm-A Powerful Therapeutic Tool for COVID-19 Patients.Biomedicines. 2023 Jun 16;11(6):1736. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11061736. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37371831 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhou D., Dejnirattisai W., Supasa P., Liu C., Mentzer A.J., Ginn H.M., Zhao Y., Duyvesteyn H.M.E., Tuekprakhon A., Nutalai R., et al. Evidence of escape of SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1.351 from natural and vaccine-induced sera. Cell. 2021;184:2348–2361.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.037. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

