Gaussian Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Simulations Investigation on the Mechanism of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) C-Domain Inhibition by Dipeptides
- PMID: 35159478
- PMCID: PMC8834632
- DOI: 10.3390/foods11030327
Gaussian Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Simulations Investigation on the Mechanism of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) C-Domain Inhibition by Dipeptides
Abstract
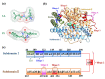
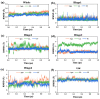
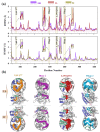
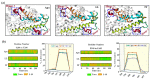
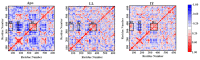
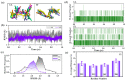
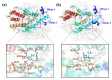
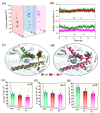
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptides extracted from food proteins can lower blood pressure by inhibiting ACE activity. A recent study showed that the inhibitory activity of IY (Ile-Tyr, a dipeptide derived from soybean protein) against ACE was much higher than that of LL (Leu-Leu), although they had similar hydrophobic and predicted activity values. It was difficult to reveal the deep molecular mechanism underlying this phenomenon by traditional experimental methods. The Apo and two complex systems (i.e., ACE-LL and ACE-IY) were therefore subjected to 1 μs long Gaussian accelerated molecular dynamics (GaMD) simulations. The results showed that the binding of IY can cause obvious contraction of the active site of ACE, mainly manifested by a significant lateral shift of α13, α14, and α15. In addition, hinge 2 and hinge 3 were more stable in the ACE-IY system, while these phenomena were not present in the ACE-LL system. Moreover, the α10 of the IY-bound ACE kept an inward state during the simulation progress, which facilitated the ACE to remain closed. However, for the LL-bound ACE, the α10 switched between two outward states. To sum up, our study provides detailed insights into inhibitor-induced conformational changes in ACE that may help in the design of specific inhibitors targeting ACE for the treatment of hypertension.
Keywords: Gaussian accelerated molecular dynamics (GaMD) simulations; angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE); inhibitory peptides; molecular mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Study on the domain selective inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) by food-derived tyrosine-containing dipeptides.J Food Biochem. 2021 Jul;45(7):e13779. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13779. Epub 2021 Jun 1. J Food Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34060658
-
Identification of post-digestion angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from soybean protein Isolate: Their production conditions and in silico molecular docking with ACE.Food Chem. 2021 May 30;345:128855. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128855. Epub 2020 Dec 10. Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 33340899
-
Measuring angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory activity by micro plate assays: comparison using marine cryptides and tentative threshold determinations with captopril and losartan.J Agric Food Chem. 2013 Nov 13;61(45):10685-90. doi: 10.1021/jf403004e. Epub 2013 Oct 31. J Agric Food Chem. 2013. PMID: 24131339
-
Considerations for Docking of Selective Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors.Molecules. 2020 Jan 11;25(2):295. doi: 10.3390/molecules25020295. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 31940798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transforming Non-Selective Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors in C- and N-domain Selective Inhibitors by Using Computational Tools.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2020;20(14):1436-1446. doi: 10.2174/1389557520666191224113830. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31889494 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploration of the Product Specificity of chitosanase CsnMY002 and Mutants Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations.Molecules. 2023 Jan 20;28(3):1048. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031048. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36770713 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the Mechanism of Interaction between Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 and Inhibitory Peptides Based on Gaussian Accelerated Molecular Dynamic Simulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 10;25(2):839. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020839. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255913 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing the Sequence Characteristics and Molecular Mechanisms of ACE Inhibitory Peptides by Comprehensive Characterization of 160,000 Tetrapeptides.Foods. 2023 Apr 7;12(8):1573. doi: 10.3390/foods12081573. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37107368 Free PMC article.
-
Ace Deficiency Induces Intestinal Inflammation in Zebrafish.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 21;25(11):5598. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115598. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891786 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vallumrd S., Oddvang T.K., Severinsson E. The Evidence of Interdisciplinary Teamwork in the Rehabilitation of Stroke Patients with Aphasia. Open J. Nurs. 2016;06:793–811. doi: 10.4236/ojn.2016.69079. - DOI
-
- Obirikorang Y., Obirikorang C., Acheampong E., Anto E.O., Asiwu R.Y. Adherence to Lifestyle Modification among Hypertensive Clients: A Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study. Open Access Libr. J. 2018;5:1–13. doi: 10.4236/oalib.1104375. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

