Smart Magnetic Nanocarriers for Multi-Stimuli On-Demand Drug Delivery
- PMID: 35159647
- PMCID: PMC8840331
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12030303
Smart Magnetic Nanocarriers for Multi-Stimuli On-Demand Drug Delivery
Abstract
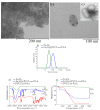
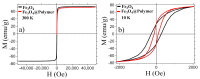
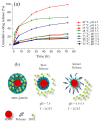
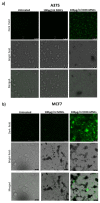
In this study, we report the realization of drug-loaded smart magnetic nanocarriers constituted by superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles encapsulated in a dual pH- and temperature-responsive poly (N-vinylcaprolactam-co-acrylic acid) copolymer to achieve highly controlled drug release and localized magnetic hyperthermia. The magnetic core was constituted by flower-like magnetite nanoparticles with a size of 16.4 nm prepared by the polyol approach, with good saturation magnetization and a high specific absorption rate. The core was encapsulated in poly (N-vinylcaprolactam-co-acrylic acid) obtaining magnetic nanocarriers that revealed reversible hydration/dehydration transition at the acidic condition and/or at temperatures above physiological body temperature, which can be triggered by magnetic hyperthermia. The efficacy of the system was proved by loading doxorubicin with very high encapsulation efficiency (>96.0%) at neutral pH. The double pH- and temperature-responsive nature of the magnetic nanocarriers facilitated a burst, almost complete release of the drug at acidic pH under hyperthermia conditions, while a negligible amount of doxorubicin was released at physiological body temperature at neutral pH, confirming that in addition to pH variation, drug release can be improved by hyperthermia treatment. These results suggest this multi-stimuli-sensitive nanoplatform is a promising candidate for remote-controlled drug release in combination with magnetic hyperthermia for cancer treatment.
Keywords: controlled drug release; drug delivery; magnetic hyperthermia; magnetite nanoparticles; pH-responsive nanocarriers; thermo-responsive nanocarriers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Blanco-Andujar C., Teran F.J., Ortega D. Current outlook and perspectives on nanoparticle-mediated magnetic hyperthermia. In: Mahmoudi M., Laurent S., editors. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Synthesis, Functionalization and Application Metal Oxides. 1st ed. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2018. pp. 197–245.
-
- Thanh N.T.K. Magnetic Nanoparticles: From Fabrication to Clinical Applications. 1st ed. CRC Press/Taylor and Francis; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2012. pp. 3–557.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

