Review on Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Materials: Bioimaging, Biosensing, Drug Delivery, Tissue Engineering, Antimicrobial, and Agro-Food Applications
- PMID: 35159802
- PMCID: PMC8839643
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12030457
Review on Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Materials: Bioimaging, Biosensing, Drug Delivery, Tissue Engineering, Antimicrobial, and Agro-Food Applications
Abstract
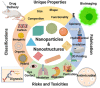
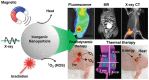
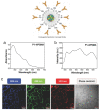
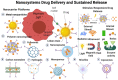
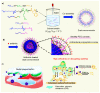
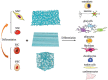
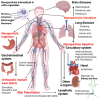
In the last few decades, the vast potential of nanomaterials for biomedical and healthcare applications has been extensively investigated. Several case studies demonstrated that nanomaterials can offer solutions to the current challenges of raw materials in the biomedical and healthcare fields. This review describes the different nanoparticles and nanostructured material synthesis approaches and presents some emerging biomedical, healthcare, and agro-food applications. This review focuses on various nanomaterial types (e.g., spherical, nanorods, nanotubes, nanosheets, nanofibers, core-shell, and mesoporous) that can be synthesized from different raw materials and their emerging applications in bioimaging, biosensing, drug delivery, tissue engineering, antimicrobial, and agro-foods. Depending on their morphology (e.g., size, aspect ratio, geometry, porosity), nanomaterials can be used as formulation modifiers, moisturizers, nanofillers, additives, membranes, and films. As toxicological assessment depends on sizes and morphologies, stringent regulation is needed from the testing of efficient nanomaterials dosages. The challenges and perspectives for an industrial breakthrough of nanomaterials are related to the optimization of production and processing conditions.
Keywords: drug delivery systems; market and regulations; nanomaterials; nanostructures; risks and toxicities; skincare; tissue-engineered scaffolds; wound dressings.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Barhoum A., Pal K., Rahier H., Uludag H., Kim I.S., Bechelany M. Nanofibers as new-generation materials: From spinning and nano-spinning fabrication techniques to emerging applications. Appl. Mater. Today. 2019;17:1–35. doi: 10.1016/j.apmt.2019.06.015. - DOI
-
- Barhoum A., El-Maghrabi H.H., Nada A.A., Sayegh S., Roualdes S., Renard A., Iatsunskyi I., Coy E., Bechelany M. Simultaneous hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions using free-standing nitrogen-doped-carbon–Co/CoOx nanofiber electrodes decorated with palladium nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2021;9:17724–17739. doi: 10.1039/d1ta03704h. - DOI
-
- Prasad S., Kumar V., Kirubanandam S., Barhoum A. Emerging Applications of Nanoparticles and Architecture Nanostructures: Current Prospects and Future Trends. Elsevier Inc.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2018. Engineered nanomaterials: Nanofabrication and surface functionalization; pp. 305–340. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

