Gender Differences in All-Cause Mortality after Acute Myocardial Infarction: Evidence for a Gender-Age Interaction
- PMID: 35159993
- PMCID: PMC8837133
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11030541
Gender Differences in All-Cause Mortality after Acute Myocardial Infarction: Evidence for a Gender-Age Interaction
Abstract
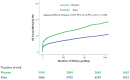
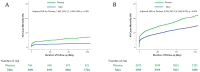
Gender difference studies in mortality after acute myocardial infarction (AMI) have shown inconsistent results. A total of 13,104 patients from the KAMIR-NIH between November 2011 and December 2015 were classified into young (n = 3837 [29.3%]) and elderly (n = 9267 [70.7%]) patients. For the study, women <65 and men <55 years of age were considered "young". In the adjusted model of the entire cohort, there was no significant difference in three-year all-cause mortality between women and men (17.8% vs. 10.3%; adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.953; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.799-1.137). However, when the entire cohort was subdivided into two age groups, young women showed an 84.3% higher mortality rate than young men (adjusted HR, 1.843; 95% CI, 1.098-3.095). Contrariwise, elderly women patients had a 20.4% lower hazard of mortality compared with elderly men (adjusted HR, 0.796; 95% CI, 0.682-0.929). The interaction of gender with age was significant, even after multiple adjustments (adjusted p for interaction = 0.003). The purpose of this study was to assess whether gender differences depend on the patients' age. Based on our analysis, higher mortality of young women remains even in the contemporary era of AMI. A better understanding of the mechanisms underlying these differences is warranted.
Keywords: acute myocardial infarction; gender differences; interaction term of gender with age.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sielski J., Kaziród-Wolski K., Jurys K., Wałek P., Siudak Z. The Effect of Periprocedural Clinical Factors Related to the Course of STEMI in Men and Women Based on the National Registry of Invasive Cardiology Procedures (ORPKI) between 2014 and 2019. J. Clin. Med. 2021;10:5716. doi: 10.3390/jcm10235716. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mehta L.S., Beckie T.M., DeVon H.A., Grines C.L., Krumholz H.M., Johnson M.N., Lindley K.J., Vaccarino V., Wang T.Y., Watson K.E., et al. Acute Myocardial Infarction in Women: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133:916–947. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000351. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dagan M., Dinh D.T., Stehli J., Tan C., Brennan A., Warren J., Ajani A.E., Freeman M., Murphy A., Reid C.M., et al. Sex Disparity In Secondary Prevention Pharmacotherapy And Clinical Outcomes Following Acute Coronary Syndrome. Eur. Heart J. Qual. Care Clin. Outcome. 2021:qcab007. doi: 10.1093/ehjqcco/qcab007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Rosa R., Morici N., De Luca G., De Luca L., Ferri L.A., Piatti L., Tortorella G., Grosseto D., Franco N., Misuraca L., et al. Association of Sex with Outcome in Elderly Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. Am. J. Med. 2021;134:1135–1141. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2021.03.025. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources