Predictors of Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcome at 6 Months after Hospitalization for COVID-19
- PMID: 35160182
- PMCID: PMC8836381
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11030729
Predictors of Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcome at 6 Months after Hospitalization for COVID-19
Abstract
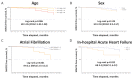
Clinical outcome data of patients discharged after Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) are limited and no study has evaluated predictors of cardiovascular prognosis in this setting. Our aim was to assess short-term mortality and cardiovascular outcome after hospitalization for COVID-19. A prospective cohort of 296 consecutive patients discharged after COVID-19 from two Italian institutions during the first wave of the pandemic and followed up to 6 months was included. The primary endpoint was all-cause mortality. The co-primary endpoint was the incidence of the composite outcome of major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE: cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, stroke, pulmonary embolism, acute heart failure, or hospitalization for cardiovascular causes). The mean follow-up duration was 6 ± 2 months. The incidence of all-cause death was 4.7%. At multivariate analysis, age was the only independent predictor of mortality (aHR 1.08, 95% CI 1.01-1.16). MACCE occurred in 7.2% of patients. After adjustment, female sex (aHR 2.6, 95% CI 1.05-6.52), in-hospital acute heart failure during index hospitalization (aHR 3.45, 95% CI 1.19-10), and prevalent atrial fibrillation (aHR 3.05, 95% CI 1.13-8.24) significantly predicted the incident risk of MACCE. These findings may help to identify patients for whom a closer and more accurate surveillance after discharge for COVID-19 should be considered.
Keywords: COVID-19; cardiovascular events; follow-up; mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest related to this paper.
Figures

References
-
- WHO WHO Weekly Epidemiological Update. 6 April 2021. [(accessed on 6 April 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on....
-
- Cummings M.J., Baldwin M.R., Abrams D., Jacobson S.D., Meyer B.J., Balough E.M., Aaron J.G., Claassen J., Rabbani L.E., Hastie J., et al. Epidemiology, clinical course, and outcomes of critically ill adults with COVID-19 in New York City: A prospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395:1763–1770. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31189-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mennuni M.G., Renda G., Grisafi L., Rognoni A., Colombo C., Lio V., Foglietta M., Petrilli I., Pirisi M., Spinoni E., et al. Clinical outcome with different doses of low-molecular-weight heparin in patients hospitalized for COVID-19. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis. 2021;52:782–790. doi: 10.1007/s11239-021-02401-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

