Association among Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction (DGBI) and Fibromyalgia: A Prospective Study
- PMID: 35160260
- PMCID: PMC8836992
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11030809
Association among Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction (DGBI) and Fibromyalgia: A Prospective Study
Abstract
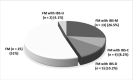
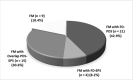
The disorders of gut-brain interaction (DGBI) have been associated with Fibromyalgia (FM). However, there are no data about the relationship between FM and DGBI using Rome IV criteria. This study aimed to evaluate the prevalence of FM in patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and/or Functional Dyspepsia (FD) and the prevalence of IBS and FD in FM patients using Rome IV criteria. DGBI patients and FM patients were recruited from two outpatient clinics devoted to DGBI and FM. All patients underwent a standardized gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms questionnaire. FM symptoms in DGBI patients were assessed through Fibromyalgia Rapid Screening Tool (FiRST) and Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire. Thereafter, the rheumatologists evaluated them. 49.0% of FM patients fulfilled the diagnostic criteria for IBS, 81.6% for FD with an overlap for both IBS/FD in 44.9%. IBS-C was the most prevalent IBS-subtype in DGBI patients, whereas IBS-M was the most prevalent in FM patients (p = 0.01). 45.3% of DGBI patients reported pathological FiRST scores. DGBI patients with FM showed the highest score at the standardized GI questionnaire followed by FM patients with DGBI and DGBI without FM. In conclusion DGBI are common in FM patients and vice versa. The presence of FD is extremely frequent in FM patients. A multidisciplinary approach should be routinely used for the management of these patients.
Keywords: fibromyalgia; functional dyspepsia; gastrointestinal diseases; irritable bowel syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Greater Overlap of Rome IV Disorders of Gut-Brain Interactions Leads to Increased Disease Severity and Poorer Quality of Life.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 May;20(5):e945-e956. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.05.042. Epub 2021 May 27. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 34052391
-
Complex and Bidirectional Interplay Between Marital Quality, Catastrophizing, Psychological Dysfunction, and Quality of Life in Married Malay Women With Disorder of Gut-Brain Interactions.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2025 Apr;37(4):e15000. doi: 10.1111/nmo.15000. Epub 2025 Jan 9. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2025. PMID: 39789879
-
Disorders of gut-brain interaction: Highly prevalent and burdensome yet under-taught within medical education.United European Gastroenterol J. 2022 Sep;10(7):736-744. doi: 10.1002/ueg2.12271. Epub 2022 Jul 3. United European Gastroenterol J. 2022. PMID: 35781806 Free PMC article.
-
Review article: epidemiology of IBS and other bowel disorders of gut-brain interaction (DGBI).Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Dec;54 Suppl 1:S1-S11. doi: 10.1111/apt.16582. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 34927754 Review.
-
Innovations in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of disorders of gut-brain interaction (DGBI).Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Jun;19(6):657-670. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2025.2508967. Epub 2025 May 21. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40390189 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of social media use in onset of functional gastrointestinal disorders in children.Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023 Jun;66(6):226-232. doi: 10.3345/cep.2022.00843. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36550775 Free PMC article.
-
Adapted Low-FODMAP Diet in IBS Patients with and without Fibromyalgia: Long-Term Adherence and Outcomes.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 9;16(19):3419. doi: 10.3390/nu16193419. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39408383 Free PMC article.
-
Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Multifaceted World Still to Discover.J Clin Med. 2022 Jul 15;11(14):4103. doi: 10.3390/jcm11144103. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35887869 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Diet and Symptom Severity in Disorder of Gut-Brain Interaction.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 15;13(14):4132. doi: 10.3390/jcm13144132. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39064172 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Fibromyalgia: Novel Nutraceutical Therapies Beyond Traditional Pharmaceuticals.Nutrients. 2025 Jan 31;17(3):530. doi: 10.3390/nu17030530. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 39940388 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Petersen M.W., Schröder A., Jørgensen T., Ørnbøl E., Meinertz D.T., Eliasen M. Irritable bowel, chronic widespread pain, chronic fatigue and related syndromes are prevalent and highly overlapping in the general population. DanFunD Sci. Rep. 2020;10:3273. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60318-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

