Green Extraction of Carrageenans from Mastocarpus stellatus
- PMID: 35160543
- PMCID: PMC8839242
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14030554
Green Extraction of Carrageenans from Mastocarpus stellatus
Abstract
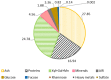
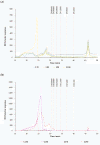
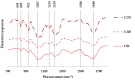
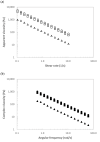
The recovery of biopolymers from natural resources using eco-friendly extraction technologies that enhance their mechanical properties has gained attention in recent years. In this context, this work deals with the isolation of hybrid carrageenans from Mastocarpus stellatus red seaweed using subcritical water extraction operating in a wide range of thermal conditions (70-190 °C). The extracted biopolymers were analyzed by means of either Fourier-Transform infrared, nuclear magnetic resonance, rheological or cell viability assays. In parallel, the fundamental chemical composition of the seaweed used as raw material, as well as the main phytochemical properties of the soluble liquid extracts, were also studied. Results indicated that thermal extraction conditions significantly affected the rheological behavior of the recovered hybrid carrageenans. The hybrid carrageenan extraction yields varied, with results between 10.2 and 30.2% being the highest values obtained at hydrothermal treatment of 130 °C. A wide palette of viscous features was identified for recovered hybrid carrageenans, with the strongest rheology properties observed at the same temperature. It should be remarked that the maximum inhibitory effect was also obtained at 130 °C for both the ovarian carcinoma cell line (A2780) (65%, IC50: 0.31 mg/mL) and lung carcinoma cell line (A549) (59%, IC50: 0.41 mg/mL).
Keywords: antioxidant; antitumoral; carrageenan; hot water extraction; mechanical properties; subcritical water extraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Choudhary B., Chauhan O.P., Mishra A. Edible Seaweeds: A Potential Novel Source of Bioactive Metabolites and Nutraceuticals With Human Health Benefits. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021;8:740054. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.740054. - DOI
-
- Qiu S.M., Aweya J.J., Liu X., Liu Y., Tang S., Zhang W., Cheong K.L. Bioactive polysaccharides from red seaweed as potent food supplements: A systematic review of their extraction, purification, and biological activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022;275:118696. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118696. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- RTI2018-096376-B-I00/Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities of Spain
- ED431F 2020/01/Consellería de Cultura, Educación e Universidade da Xunta de Galicia
- RYC2018-024454-I/Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities of Spain
- ED481B 2018/071/Consellería de Cultura, Educación e Universidade da Xunta de Galicia
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

