Unraveling of Advances in 3D-Printed Polymer-Based Bone Scaffolds
- PMID: 35160556
- PMCID: PMC8840342
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14030566
Unraveling of Advances in 3D-Printed Polymer-Based Bone Scaffolds
Abstract
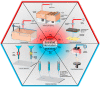
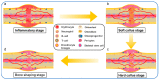
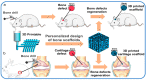
The repair of large-area irregular bone defects is one of the complex problems in orthopedic clinical treatment. The bone repair scaffolds currently studied include electrospun membrane, hydrogel, bone cement, 3D printed bone tissue scaffolds, etc., among which 3D printed polymer-based scaffolds Bone scaffolds are the most promising for clinical applications. This is because 3D printing is modeled based on the im-aging results of actual bone defects so that the printed scaffolds can perfectly fit the bone defect, and the printed components can be adjusted to promote Osteogenesis. This review introduces a variety of 3D printing technologies and bone healing processes, reviews previous studies on the characteristics of commonly used natural or synthetic polymers, and clinical applications of 3D printed bone tissue scaffolds, analyzes and elaborates the characteristics of ideal bone tissue scaffolds, from t he progress of 3D printing bone tissue scaffolds were summarized in many aspects. The challenges and potential prospects in this direction were discussed.
Keywords: 3D printing; bone healing; bone tissue engineering scaffolds; polymer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Tuan Rahim T.N.A., Abdullah A., Md Akil H., Mohamad D., Rajion Z. The improvement of mechanical and thermal properties of polyamide 12 3D printed parts by fused deposition modelling. Express Polym. Lett. 2017;11:963–982. doi: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2017.92. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

