Polysaccharides Used in Biosorbents Preparation for Organic Dyes Retaining from Aqueous Media
- PMID: 35160577
- PMCID: PMC8839637
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14030588
Polysaccharides Used in Biosorbents Preparation for Organic Dyes Retaining from Aqueous Media
Abstract
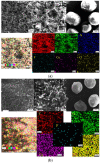
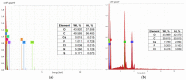
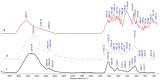
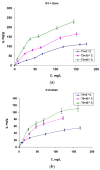
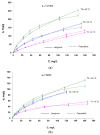
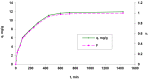
Natural polymers can themselves be efficient as materials with biosorptive properties but can also be used to transform microbial biomass into an easy-to-handle form, respectively, into biosorbents, through immobilization. The article aims to study biosorbents based on residual microbial biomass (Saccharomyces pastorianus yeast, separated after the brewing process by centrifugation and dried at 80 °C) immobilized in sodium alginate. The biosorptive properties of this type of biosorbent (spherical particles 2 and 4 mm in diameter) were studied for removal of reactive dye Brilliant Red HE-3B (with concentration in range of 16.88-174.08 mg/L) from aqueous media. The paper aims at three aspects: (i) the physico-chemical characterization of the biosorbent (Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) and Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectra); (ii) the modeling of biosorption data in order to calculate the quantitative characteristic parameters using three equilibrium isotherms (Langmuir, Freundlich, and Dubinin-Radushkevich-DR); and (iii) the evaluation of thermal effect and the possible mechanism of action. The results of the study showed that biosorption capacity evaluated by Langmuir (I) model is 222.22 mg/g (ϕ = 2 mm) and 151.51 mg/g (ϕ = 4 mm) at 30 °C, and the free energy of biosorption (E) is in the range of 8.45-13.608 KJ/mol (from the DR equation). The values of thermodynamic parameters suggested an exothermic process due the negative value of free Gibbs energy (ΔG0 = -9.031 kJ/mol till -3.776 kJ/mol) and enthalpy (about ΔH0 = -87.795 KJ/mol). The obtained results underline our finding that the immobilization in sodium alginate of the residual microbial biomass of Saccharomyces pastorianus led to an efficient biosorbent useful in static operating system in the case of effluents with moderate concentrations of organic dyes.
Keywords: Saccharomyces pastorianus immobilized; biosorption; organic dye; polysaccharides as biosorbent; sodium alginate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Statistical Analysis and Optimization of the Brilliant Red HE-3B Dye Biosorption onto a Biosorbent Based on Residual Biomass.Materials (Basel). 2022 Oct 14;15(20):7180. doi: 10.3390/ma15207180. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36295248 Free PMC article.
-
Biosorbents Based on Biopolymers from Natural Sources and Food Waste to Retain the Methylene Blue Dye from the Aqueous Medium.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jul 3;14(13):2728. doi: 10.3390/polym14132728. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808773 Free PMC article.
-
Composites Based on Natural Polymers and Microbial Biomass for Biosorption of Brilliant Red HE-3B Reactive Dye from Aqueous Solutions.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Dec 9;13(24):4314. doi: 10.3390/polym13244314. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34960864 Free PMC article.
-
Biosorbent Based on Poly(vinyl alcohol)-Tricarboxi-Cellulose Designed to Retain Organic Dyes from Aqueous Media.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Jan 31;15(3):715. doi: 10.3390/polym15030715. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36772016 Free PMC article.
-
Polysaccharides as Support for Microbial Biomass-Based Adsorbents with Applications in Removal of Heavy Metals and Dyes.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Aug 27;13(17):2893. doi: 10.3390/polym13172893. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34502933 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Sustainable Solution for the Adsorption of C.I. Direct Black 80, an Azoic Textile Dye with Plant Stems: Zygophyllum gaetulum in an Aqueous Solution.Molecules. 2024 Oct 11;29(20):4806. doi: 10.3390/molecules29204806. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39459176 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical Analysis and Optimization of the Brilliant Red HE-3B Dye Biosorption onto a Biosorbent Based on Residual Biomass.Materials (Basel). 2022 Oct 14;15(20):7180. doi: 10.3390/ma15207180. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36295248 Free PMC article.
-
Modified Polymeric Biosorbents from Rumex acetosella for the Removal of Heavy Metals in Wastewater.Polymers (Basel). 2022 May 28;14(11):2191. doi: 10.3390/polym14112191. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35683864 Free PMC article.
-
Biosorbents Based on Biopolymers from Natural Sources and Food Waste to Retain the Methylene Blue Dye from the Aqueous Medium.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jul 3;14(13):2728. doi: 10.3390/polym14132728. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Filote C., Rosca M., Hlihor R.M., Cozma P., Simion I.M., Apostol M., Gavrilescu M. Sustainable Application of Biosorption and Bioaccumulation of Persistent Pollutants in Wastewater Treatment: Current Practice. Processes. 2021;9:1696. doi: 10.3390/pr9101696. - DOI
-
- Suteu D., Blaga A.C., Zaharia C. The action of microorganisms from organic pollutants in water, air, soil (Chapter 12) In: Zaharia C., editor. Current Topics, Concepts and Research Priorities in Environmental Chemistry. Volume II. Universitatii ‘Al.I. Cuza’; Iasi, Romania: 2013. pp. 259–274.
-
- Rusu L., Grigoraș C.-G., Suceveanu E.M., Simion A.-I., Dediu Botezatu A.V., Istrate B., Doroftei I. Eco-Friendly Biosorbents Based on Microbial Biomass and Natural Polymers: Synthesis, Characterization and Application for the Removal of Drugs and Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. Materials. 2021;14:4810. doi: 10.3390/ma14174810. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

