Alginate Hydrogels with Aloe vera: The Effects of Reaction Temperature on Morphology and Thermal Properties
- PMID: 35160695
- PMCID: PMC8836575
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15030748
Alginate Hydrogels with Aloe vera: The Effects of Reaction Temperature on Morphology and Thermal Properties
Abstract
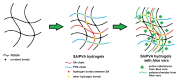
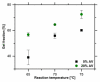
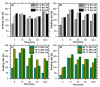
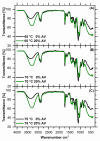
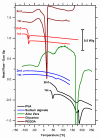
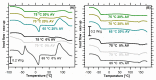
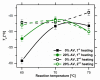
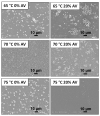
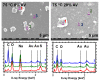
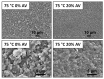
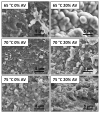
In this study, we investigated the impact of reaction temperature on the physicochemical, structural, morphological, and thermal properties of sodium alginate/poly (vinyl alcohol)-based hydrogels, both in the pure form and with the addition of 20% (v/v) Aloe vera solution. The materials were prepared by chemical crosslinking at temperatures in the range of 65-75 °C. Poly (ethylene glycol) diacrylate was used as a crosslinking agent. The extent to which the crosslinking reaction proceeded was studied as a function of the reaction temperature, along with the thermal properties and morphology of the final materials. A measurement of gel fraction, in agreement with differential scanning calorimetry and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, showed that a higher temperature of reaction promoted the crosslinking reaction. On the basis of the aforementioned techniques, as well as by energy dispersive X-ray analysis under an electron microscope, it was also shown that the bioadditive Aloe vera promoted the crosslinking reaction.
Keywords: Aloe vera; DSC analysis; hydrogels; sodium alginate/poly (vinyl alcohol) matrix.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Varghese S.A., Rangappa S.M., Siengchin S., Parameswaranpillai J. Hydrogels Based on Natural Polymers. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2019. Natural polymers and the hydrogels prepared from them; pp. 17–47. - DOI
-
- Olatunji O. Natural Polymers Industry Techniques and Applications. Springer International Publishing; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2016. Classification of Natural Polymers; pp. 1–17.
-
- Rajeswari S., Prasanthi T., Sudha N., Swain R.P., Panda S., Goka V. Natural polymers: A recent review. World J. Pharm. Sci. 2017;6:472–494. doi: 10.20959/wjpps20178-9762. - DOI
-
- Gyles D.A., Castro L.D., Carréra Silva J.O., Jr., Ribeiro-Costa R.M. A review of the designs and prominent biomedical ad-vances of natural and synthetic hydrogel formulations. Eur. Polym. J. 2017;88:373–392. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2017.01.027. - DOI
-
- Saini K. Preparation method, properties and crosslinking of hydrogel: A review. PharmaTutor. 2017;5:27–36.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

