Poly-Lysine Dendritic Nanocarrier to Target Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Overexpressed Breast Cancer for Methotrexate Delivery
- PMID: 35160746
- PMCID: PMC8836561
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15030800
Poly-Lysine Dendritic Nanocarrier to Target Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Overexpressed Breast Cancer for Methotrexate Delivery
Abstract
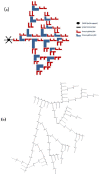
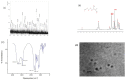
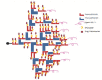
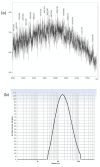
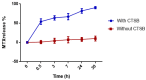
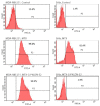
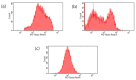
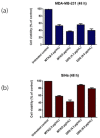
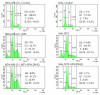
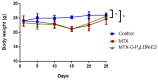
A fourth generation poly-lysine dendritic nanocarrier (P4LDN)-based targeted chemotherapy for breast cancer is attempted by incorporating an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-specific short peptide E2 (ARSHVGYTGAR) and the drug methotrexate (MTX) into a nanocarrier system. The drug is incorporated into the nanocarrier using a cathepsin B cleavable spacer: glycine-phenylalanine-leucine-glycine (GFLG). The in vitro analysis of the time-dependent drug release, binding and internalization ability, and the cytotoxic nature showed that this drug delivery system (DDS) is highly effective. The efficacy analysis using non-obese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficiency (NOD-SCID) mice also showed that compared to the control group, the DDS can effectively reduce tumor volume. The mice that received the DDS appeared to gain weight more rapidly than the free drug, which suggests that the dendrimer is more easily tolerated by mice than the free drug.
Keywords: breast cancer; epidermal growth factor receptor; in silico approach; in vivo evaluation; methotrexate; poly-lysine dendritic nanocarrier; solid-phase peptide synthesis; targeted drug delivery; tetrapeptide spacer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
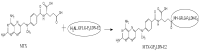




References
-
- Gewirtz D.A., Bristol M.L., Yalowich J.C. Toxicity issues in cancer drug development. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2010;11:612–614. - PubMed
-
- Boyd B.J., Kaminskas L.M., Karellas P., Krippner G., Lessene R., Porter C.J. Cationic Poly-l-lysine Dendrimers: Pharmacokinetics, Biodistribution, and Evidence for Metabolism and Bioresorption after Intravenous Administration to Rats. Mol. Pharm. 2006;3:614–627. doi: 10.1021/mp060032e. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang S., Chen R. pH-Responsive, Lysine-Based, Hyperbranched Polymers Mimicking Endosomolytic Cell-Penetrating Peptides for Efficient Intracellular Delivery. Chem. Mater. 2017;29:5806–5815. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b00054. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

